Accident prevention: AI as a tool for preventing road tragedies
Current problems and the need for innovative solutions
The increase in traffic and the complexity of interactions on the road have led to an accident-prone scenario on our roads. Traditional solutions are not sufficient to address road safety in a comprehensive manner. A significant transformation is required that not only addresses the consequences of accidents, but also prevents their occurrence.
Innovations in in-vehicle AI and V2I technology
Driver assistance systems, collision detection and autonomous driving have emerged as essential elements to improve road safety. The integration of AI in vehicles benefits drivers as well as pedestrians and cyclists. These technologies work proactively to prevent accidents and reduce the risk of collisions and collisions.
Technological advances in vehicles are not only limited to autonomous or driver assistance capabilities. Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication systems are also being developed to enable more seamless interaction between vehicles and road infrastructure.
V2I systems allow vehicles to communicate with the surrounding road infrastructure, such as traffic lights, traffic signs and traffic management systems. This means that drivers can receive real-time information about road conditions, such as road works in progress, accidents or congestion, allowing them to make more informed and safer decisions.
In addition, V2I systems can facilitate the implementation of more efficient traffic management technologies, such as traffic light coordination to reduce congestion and improve vehicle flow. They can also help improve road safety by alerting drivers to risky situations, such as construction zones or dangerous intersections. Thanks to AI, car companies can manage road data, improvements in manufacturing and maintenance processes, and useful statistics for both their devices and administrations.

The need for AI data for administrators and policy makers
AI provides valuable information on traffic patterns, critical risk points and driving behaviour. Real-time data is essential for developing strategies and policies to improve road safety and reduce the number of accidents. Collaboration between AI and traffic authorities is essential to implement effective measures to prevent accidents and save lives.
In road safety management, data is essential and artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in its analysis. Here we explain how this data can help administrations and authorities:
- Risk point prediction:AI analyses historical accident data and traffic patterns to identify areas with a high probability of accidents in the future. This information allows preventive measures, such as changes in signage or improvements to road infrastructure, to be implemented to reduce the risk of accidents at these hotspots.
- Traffic optimisation:Data collected through traffic sensors and monitoring systems feed AI algorithms that can predict congestion patterns and traffic flow. This helps adjust traffic light timing and divert traffic to alternative routes, minimising congestion and improving transport efficiency.
- Identification of high-risk drivers:AI analyses driving behaviour data to identify drivers with risky driving habits, such as speeding or inadequate following distance. This information allows authorities to target enforcement to those drivers who pose the greatest threat to road safety.
- Evaluation of safety measures:Collecting data on the implementation of road safety measures, such as changes in signage or new speed regulations, allows authorities to evaluate their effectiveness. By analysing how accident and traffic patterns change before and after the implementation of these measures, authorities can make informed decisions on where and how to allocate resources to improve road safety.
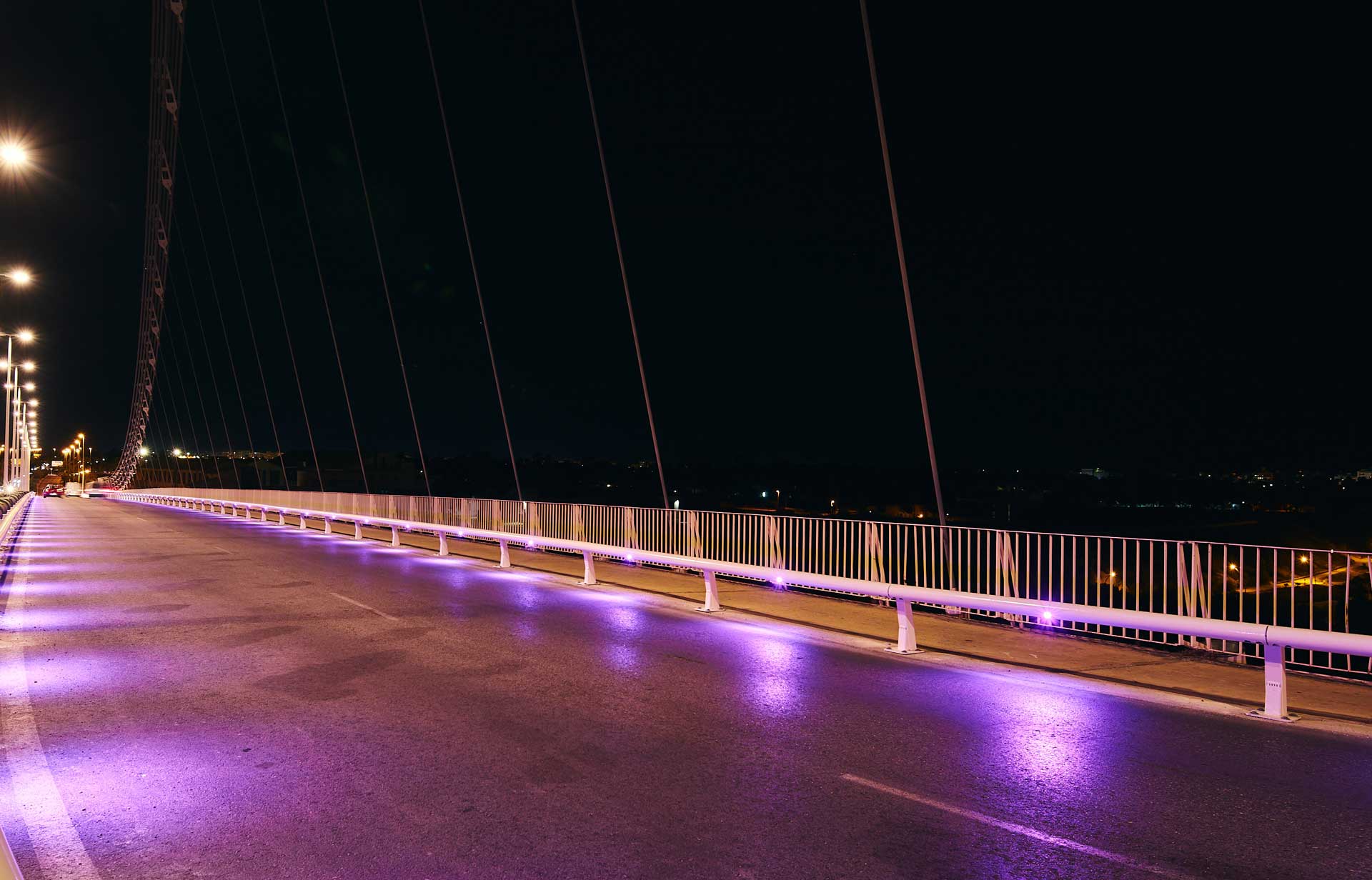
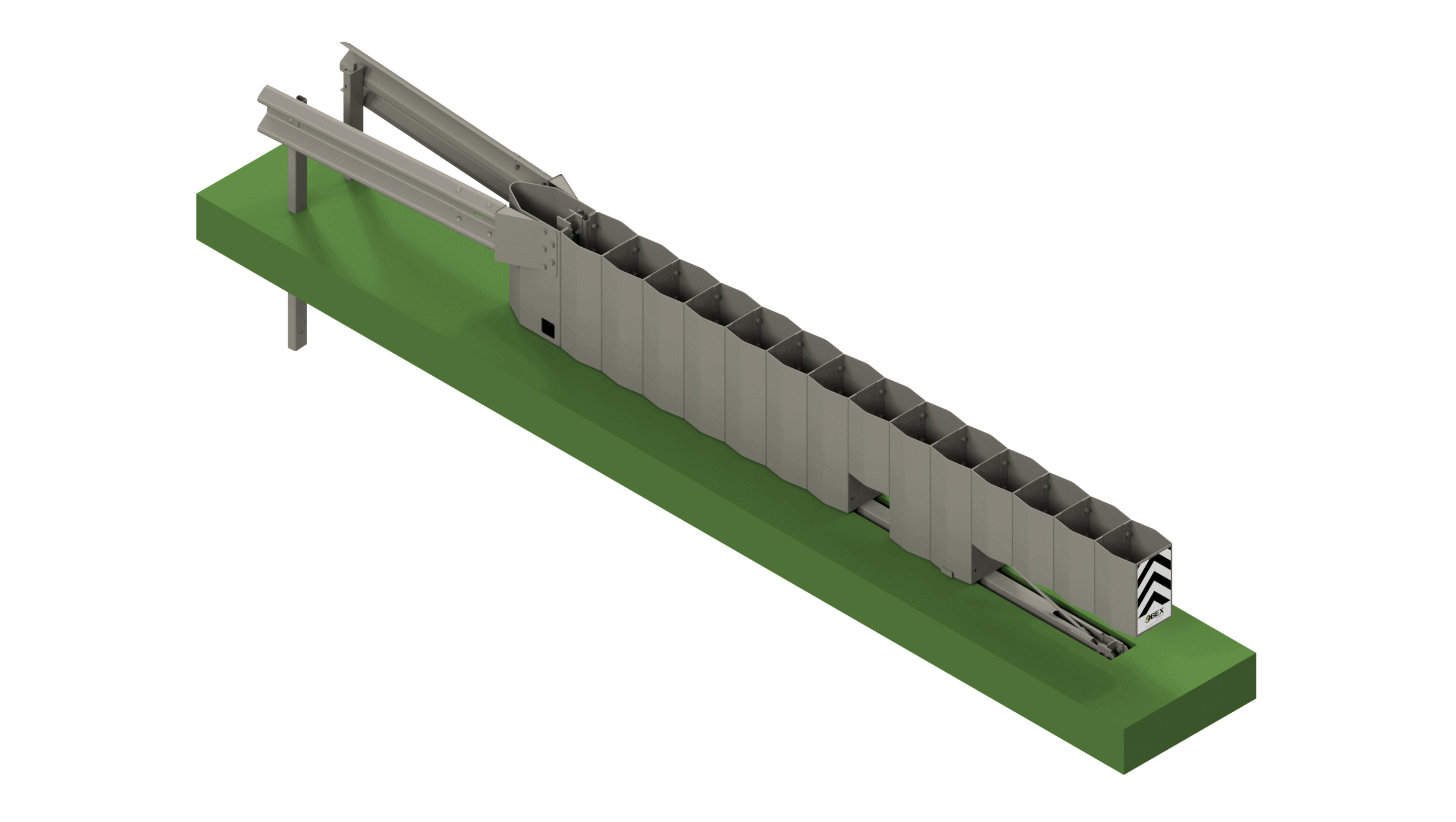
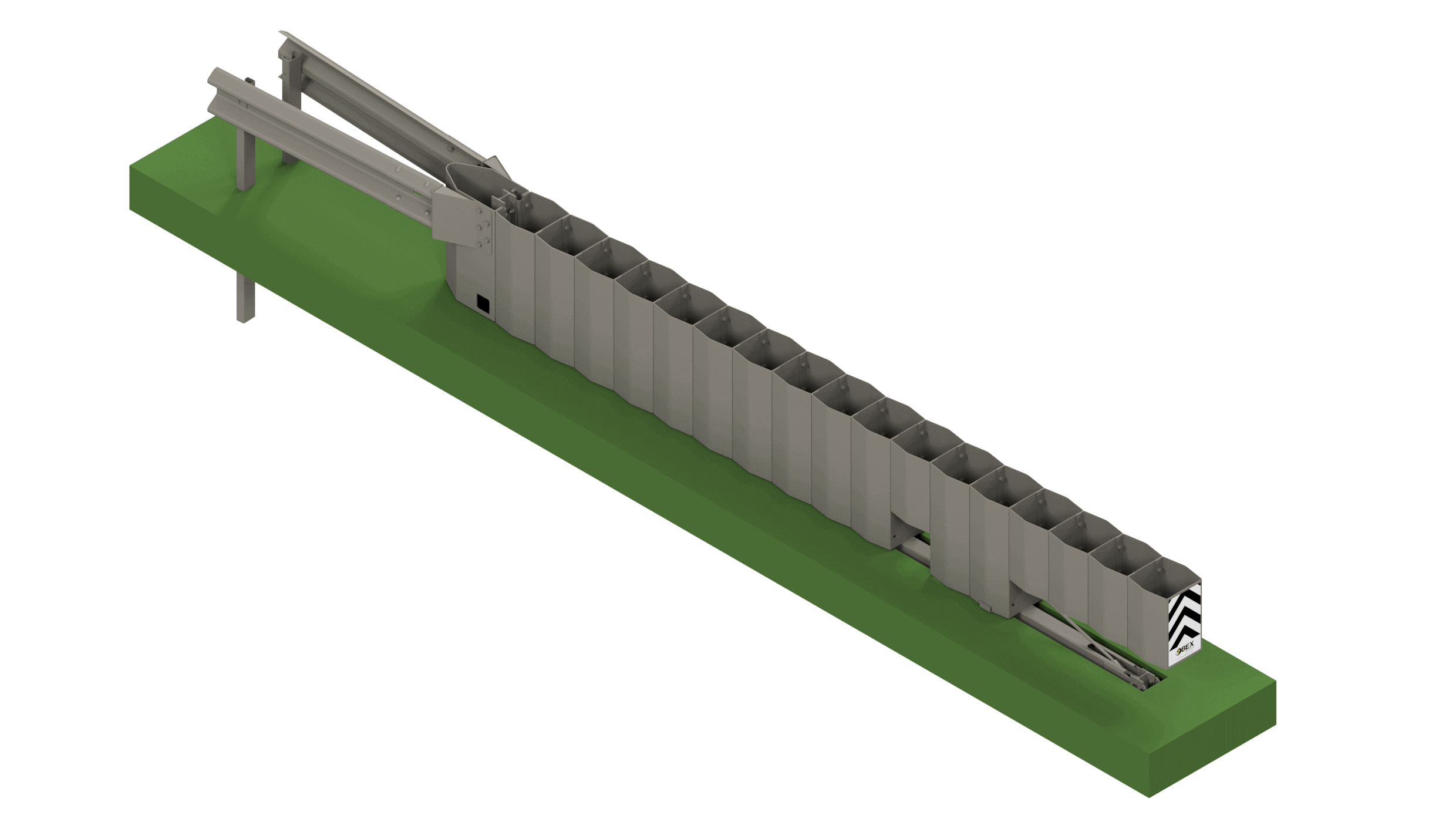
Example of the digitisation of road safety systems using IoT technology - Metaurban® SMART
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=12oqSvuo2e4
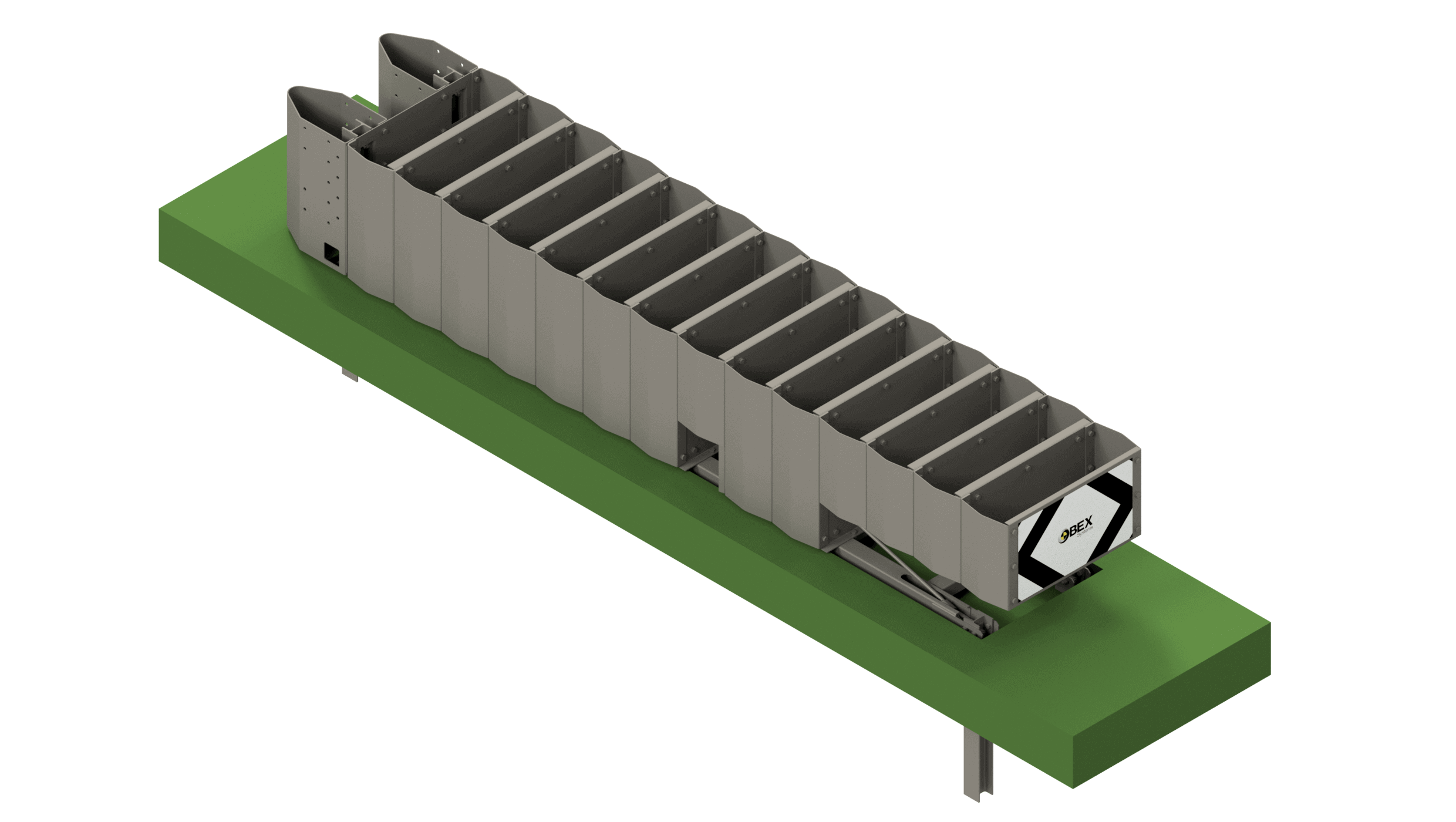
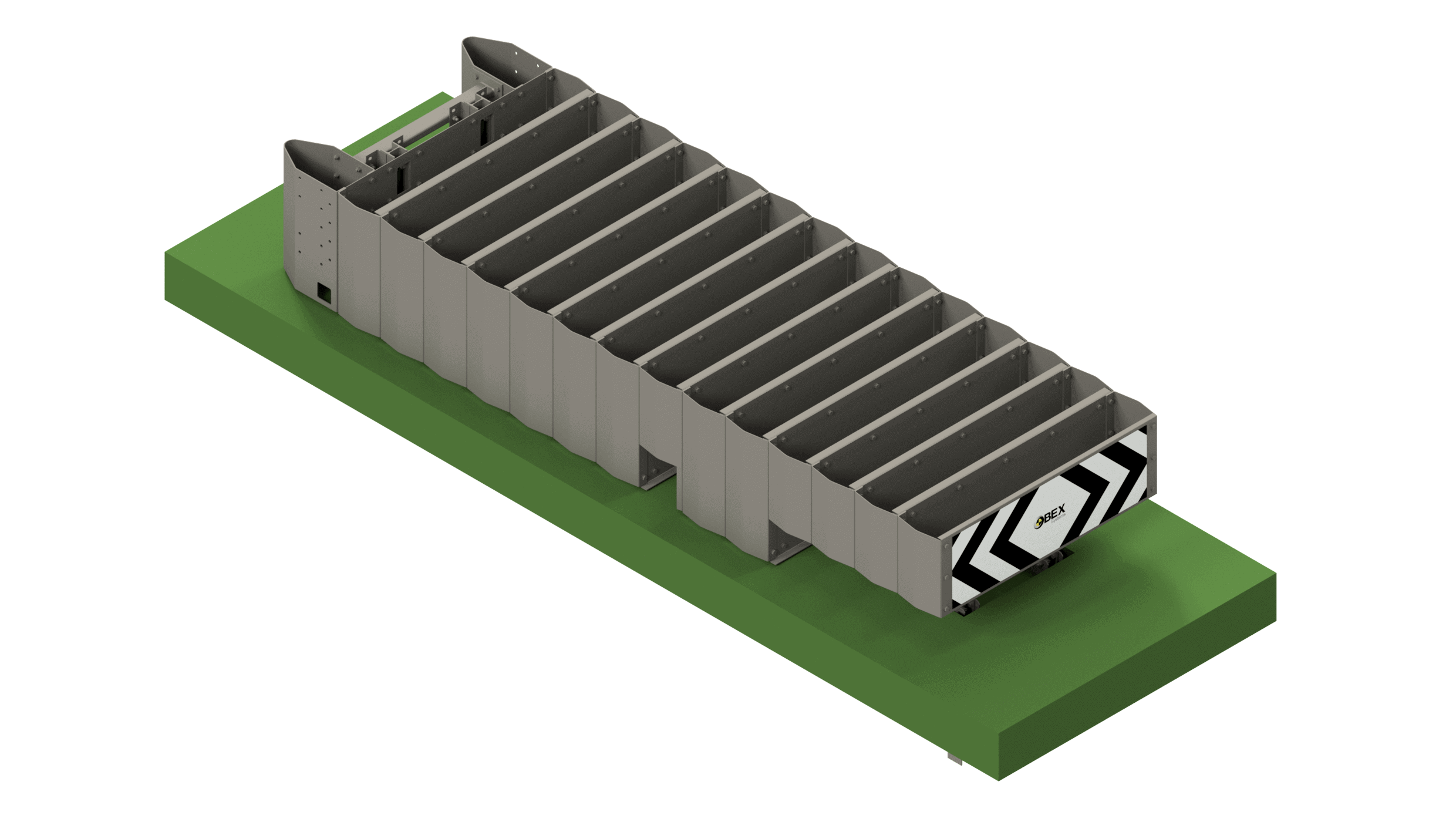
Today's digital and communications technology is sufficiently mature and has a sufficient economy of scale to design specific solutions that provide added value to road and urban equipment. Its potential is very large and varied, from the detection of risk situations on the road and their real-time warning to users, to the detection of events and useful data for the administration in order to make better decisions in mobility management. The Metaurban® SMART parapet, developed and patented by Metalesa, combines the classic benefits of a restraint system approved according to UNE EN1317 (which provides passive road safety), with PLUG&META® technology that provides added value in several areas:
- Accident and run-over prevention.
- Automatic notification in case they happen.
- Capture of data and events as useful information.
- Remote management of signalling.
Installation in urban and metropolitan areas ensures the protection of pedestrians and cyclists. Metaurban® SMART acts as an active road safety measure, making it an essential component of a safer road environment.
The future of road safety: Protecting and engaging with citizens
Reducing road crashes leads to fewer injuries, less congestion on the roads and a quieter, more efficient road environment. It improves the safety of pedestrians and cyclists, promoting a safer and more sustainable environment for all road users.
The future of road safety depends on a collective commitment to further progress in the development and implementation of innovative solutions. The continued integration of AI on our roads, together with solutions such as Metaurban® SMART, brings us closer to a scenario where traffic accidents are a concern of the past.
Changes in the regulations on barrier transitions and terminals
When talking about vehicle containment systems, the first thing that comes to mind are safety barriers and parapets. These linear elements are installed on the edges of roads to prevent vehicles from leaving the road and causing serious accidents. Although these are the first that come to mind, there are also other types of vehicle containment systems, such as impact attenuators, transitions between systems, barrier terminals, removable barrier sections and protection systems. of motorcyclists.
All of these systems are regulated by different European regulations that establish the requirements that must be met to be classified in one of the categories contemplated by said regulations. In the case of transitions and barrier terminals, the reference standard is UNE-ENV 1317-4:2002 and in this article we want to talk to you in a little more detail about the changes that are to come.
This standard, which has been in force since April 30, 2002, has never been harmonized by UNE-EN 1317-5:2008+A2:2012. This means that any Transition or Terminal that meets the tests specified in said standard will be accepted, but will not have the CE marking. Therefore, this standard is voluntary and there is no clear impulse on the part of the administrations to require this type of products evaluated under the protection of this standard.
This situation gives rise to points on the State Highway Network that are not well resolved and that can cause serious accidents.

The need to modify this regulation
The European standardization committee “CEN/TC 226/WG 1 – Crash barriers, safety fences, guard rails and bridge parapets” is responsible for preparing regulations relating to the field of vehicle containment systems. The CTN 135 Road Signage Equipment Committee hangs directly from this committee. SC1 Safety Barriers, of which the Metalesa team is a member.
For years, work has been going on within TC226 to modify the UNE-ENV 1317-4:2002 regulations to somehow remove the vehicle containment systems it regulates from the regulatory block. However, to date this task had not been achieved successfully as it was a complex task.
Transitions and terminals, by definition, connect to other systems. A transition is a longitudinal section that joins two systems, such as barriers or parapets, using special pieces that guarantee a logical transition of rigidities. A barrier terminal is a point system, such as an impact attenuator, that connects to a barrier or parapet. Therefore, the evaluation of a barrier terminal involves evaluating the connection between the barrier or parapet and the terminal, which is equivalent to evaluating a transition between systems, even if one of them is not a barrier or parapet.
When it comes to harmonizing these systems under the same standard, there is a big step that must be overcome: there are a multitude of barriers, parapets and terminals on the market that, as we have said before, comply with the regulations but do not have CE marking, which which makes it tremendously complex to establish clear rules to evaluate them and not limit free competition.
New regulations on transitions and barrier terminals on the way
Once the variability in this type of products is understood, it is understood how complex it is to regulate them, however, last June the deadline for voting in TC226 ended. This vote examined the publication of reports and technical specifications that establish the evaluation methods of each of these systems separately and facilitate administrations in establishing criteria to demand the different benefits of the systems, definitively separating them from the marking. EC.
The new regulations of these systems would be as follows:
- Barrier terminals are regulated by FprCEN/TS 1317-7. It is a technical specification, so every 3 years it is decided whether it becomes a standard to be harmonized and be able to have the CE marking.
- Transitions are regulated by FprCEN/TR 1317-10. In this case it is a Technical Report, that is, it does not have to be reviewed at any time, being a declaration of intentions regarding the fact that the transitions will not have CE marking.
With this change in the paradigm of the regulations of Barrier Terminals and Transitions, administrations no longer have to demand a CE marking that could not be obtained, since UNE-ENV 1317-4:2002 is repealed.
Finally, it should be noted that now it is the turn of the administrations to pick up the gauntlet and establish what tests or requirements are required for this type of products to be installed on the roads they regulate. Some administrations, such as the French one, have already championed this change and have requirements aligned with the new regulations.
Active Road Safety, how this new concept is transforming roads
Technology is progress, and progress makes us evolve as a society. Thanks to technological advances, new forms of communication and mobility have been created that have devised new concepts. For example, in the case of vehicles, new technologies such as electric propulsion have become popular, giving birth to personal mobility vehicles (PMV).
PMVs are becoming more common within cities and have generated a new mobility ecosystem that is presenting new challenges. The current road network has to adapt to these new habits. This means that there are new elements at stake, raising possible accidents that make it necessary to take another step-in accident prevention.
Active Road Safety, a new way of understanding accident prevention
At Metalesa, our commitment has always been to improve people's quality of life. One of our goals is to act by offering protection solutions in any of its fields. Whether it is acoustic or road protection, we always try to offer the best solutions. As our claim says: Protection, our goal.
This is why, due to the evolution of society, technology, and connection networks that already allow us to achieve 5G transfer speeds, we wanted to go one step further in our objective and consider an assumption: how can we mitigate the severity of the accidents? Could we prevent them? How can the authorities act at the time of an accident without the need for them to receive a phone call? This is what we have coined under the concept of Active Road Safety.
What is Active Road Safety?
Active Road Safety is a new concept that raises road safety to a new level. With the use of connected equipment, it is capable of collecting traffic and environment data, analyzing it in real time and notifying all road users if there is a risk of an accident due to poor visibility, traffic jams, among many other cases without intervention. from third parties.
In addition, connectivity means that in the event of an impact or risk detected on the road, the equipment may be able to notify the authorities autonomously and, on the spot, so that they can quickly manage the necessary assistance.
Differences between Road Safety and Active Road Safety
Until now, road safety equipment had a passive role in accident prevention. In the event of a vehicle impact, its task was to mitigate the severity of the accident, absorbing part of the energy and preventing the vehicle from leaving the road.
With Active Road Safety, road safety equipment starts to take an active role on the road, being able to collect data with the integrated sensors, analyze it and adapt its characteristics autonomously to communicate with road users through lights or being able to coordinate with other information elements such as variable signaling panels.
In this way, in addition to being able to communicate with road users, it is also capable of communicating with the authorities and traffic management centers. You can notify an accident in real time, collect traffic or air quality data and notify according to pre-established parameters.
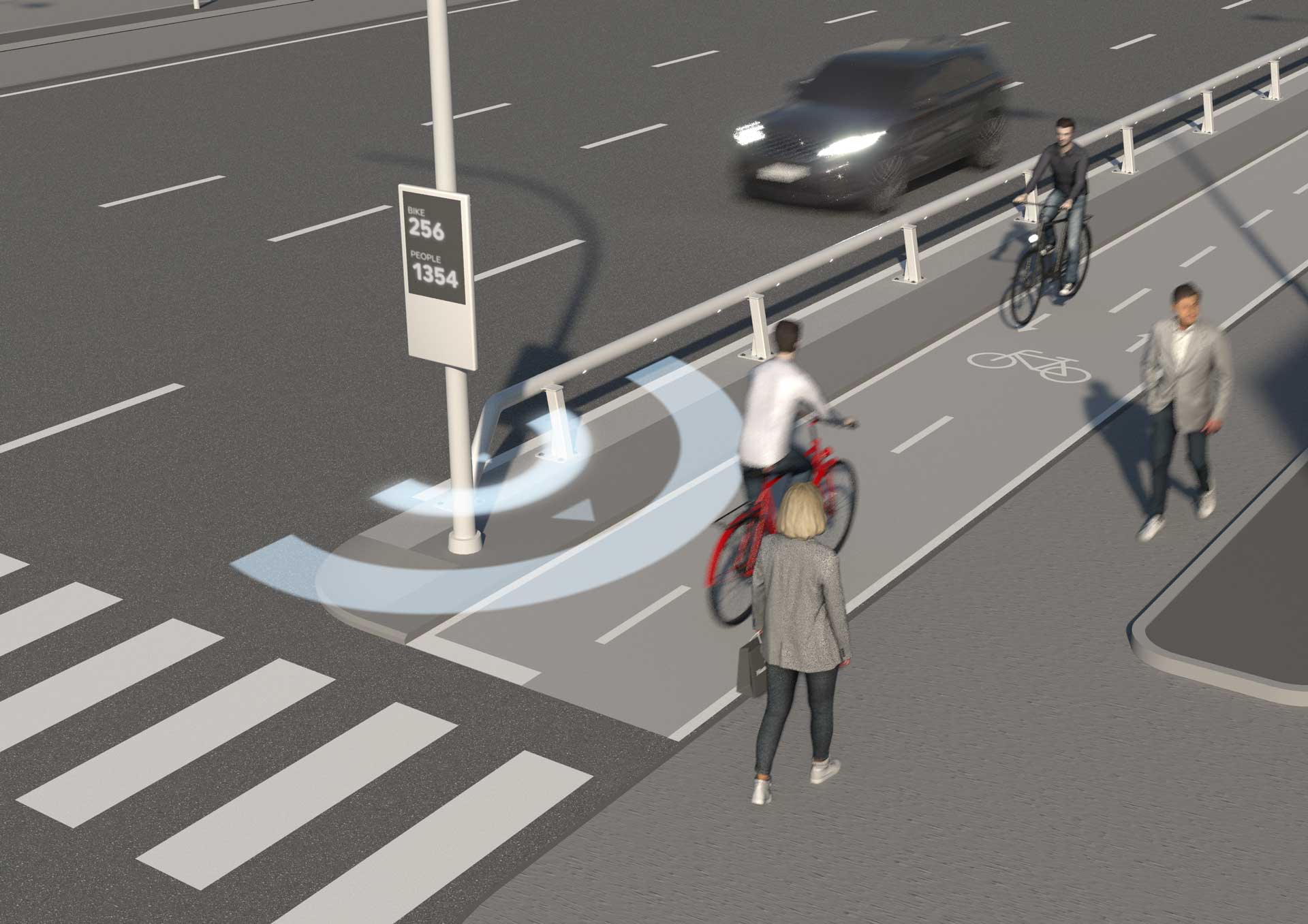

Environments of action of Active Road Safety for infrastructures
Roads are a space shared by different types of vehicles and users, from cars or trucks to smaller ones such as VMP, bicycles or even pedestrians. This means that there are a series of factors that can put the safety of users at risk, such as speeding, non-segregation of lanes, dangerous curves or sections with reduced visibility.
If we make a list of all these factors, the following would be the most important:
- Weather conditions with reduced visibility, such as fog. The reduction of visibility in the wagon is a key factor in the event of an accident, since the driver does not have a good area of visibility.
- Dangerous curves or uneven road sections. These situations can lead to accidents due to loss of control of the vehicle.
- Traffic funnels and retentions. Heavy traffic and congestion can increase the risk of accidents and decrease the efficiency of circulation. Users in a state of stress may disobey road safety precautions.
- Accidents in interurban areas. The lack of signaling and indication in certain urban areas can cause serious accidents that directly affect our citizens.
How does Active Road Safety solve problems on the road?
One of the advantages of Active Road Safety is that it can be adapted to road conditions. For example, in heavy rain, adaptive lighting systems can be adjusted to improve driver visibility and reduce the risk of accidents. Similarly, in low visibility situations due to fog or ice, sensors can detect these conditions and alert the driver to exercise caution.
Another advantage of Active Road Safety is that the risk of accidents and injuries can be reduced. Implementing specific road safety measures can help prevent accidents and minimize the impact should one occur. For example, the installation of safety barriers and warning signs on dangerous curves or uneven sections of road can prevent vehicles from running off the road in the event of driver error.
In addition, Active Road Safety can also improve traffic efficiency. For example, real-time traffic information systems can help drivers avoid traffic jams and congestion, reducing travel time and improving the efficiency of driving on the road.
If you want to find out more about this new concept and find out how Metalesa is working to make it a reality, you can consult our microsite on Active Road Safety, where we talk in more detail.
For a safe Christmas on the road
We are approaching the Christmas holidays, when we usually meet with our loved ones, sometimes traveling many kilometres to be back home for some days. For us, the best Christmas gift is that all drivers arrive safely at their destinations.
Data that, even if you don't like it, we have to tell you
According to the DGT, last Christmas 57 fatalities were settled in traffic accidents on Spanish roads. Most of the accidents involved loss of control and run-off-road collisions. 21 people were vulnerable users (pedestrians, motorists and cyclists) while 35 were vehicle drivers.
This is not data kind to say, but, if we want to make drivers aware of the importance of being careful on the road this Christmas, it is necessary to expose the reality as hard as it is. Hopefully this year this figure is reduced to the minimum possible. Let's do our best to achieve this goal.

Traffic accidents: why do they happen more at Christmas time?
- At Christmas trips increase, up to a 16 million estimation. The more cars out there, the more chances of suffering an accident, so it is essential to exercise extreme caution at the wheel.
- Increase in alcohol consumption: Christmas lunches and dinners stand out for their joy, delicious food, and as a general rule, a few extra drinks. Something as simple and effective as the famous 'if you drink, don't drive', unfortunately it is not followed literally, and every Christmas, a considerable number of drivers test positive for breathalyzer, posing a great danger to safety drivers and themselves.
- Adverse weather conditions: Winter weather can play against us. Strong winds, icy roads, fog or rain multiply the danger on the roads. These adverse weather conditions make it difficult to control the vehicle and can trigger accidents, so it is important to slow down, keep a safe distance from other vehicles and drive with all 5 senses on the road.
- Speeding: Speeding is the leading cause of traffic accidents at Christmas. These are dates when we tend to get overwhelmed by last minute purchases and the unexpected ... But rushing on the road is never a good option. Think before acting!
With all these factors in mind on the road, we can all have a happy Christmas free of bad news. These dates are to be enjoyed to the fullest!

Protection is our goal: Discover our products
Whether it is Christmas or not, whatever the date, road safety does not understand holidays and we are always there. Our products, both on Spanish and international roads, take care of the people who travel every day, protecting people, saving lives.
Next, we show you some of the products that we design, manufacture and install at Metalesa to guarantee the safety of what matters most to us: people. Because you deserve a Christmas full of love and happiness.
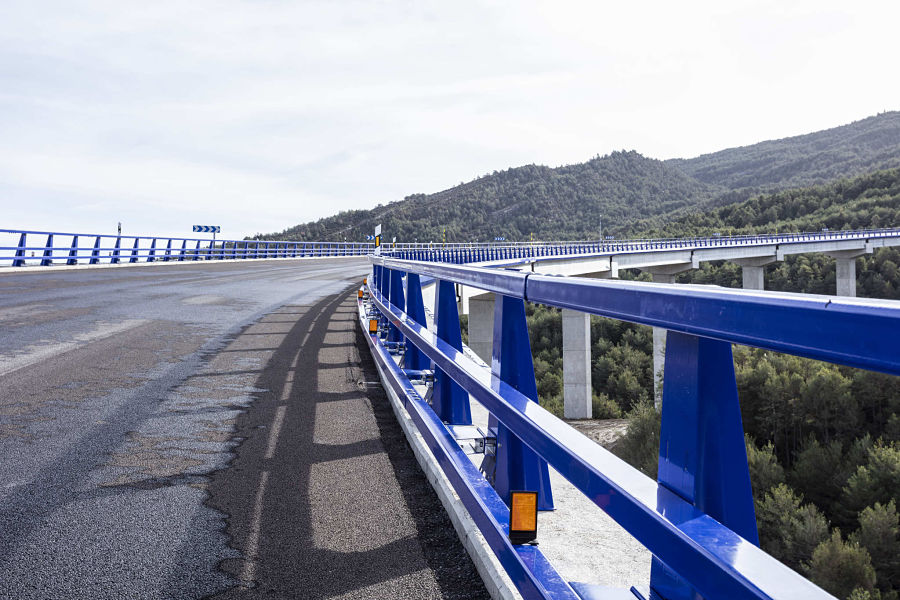
Bridge equipment
The bridges on the roads represent sections of more danger for drivers, therefore, we take care of providing them with protection measures through the installation of equipment for bridges.
Bridge Metal parapets
A metal parapet is a vehicle restraint system approved according to the UNE EN 1317 parts 1 and 2 standard, so that having passed the relevant full-scale tests it has obtained the CE marking. It is placed in passage works, wall crowning, bridge decks ...
We have the META13 bridge parapet and the META16 metal parapet, essential as elements to guarantee road safety.
Some of its advantages:
- Both parapets allow the placement of acoustic screens and vandal-proof fences at a very short distance from the parapet.
- In the event of a vehicle crash, replacement of items is quick and inexpensive.
- It is very versatile with the possibility of placing grilles or protection systems for motorists
- High durability through discontinuous galvanization, allows thermo-lacquering in the different colors of the RAL chart.

Railings for bridges
Bridge rails function as a restraint system for people or other personal mobility vehicles.
We have a wide variety of models of steel railing for bridges that are easy to install, being able to choose the most suitable thermo-lacquered finishes and colors for the integration of the railing with the landscape.
We also manufacture stainless steel railings, with steel cable or other designs that will cover any project requirement.

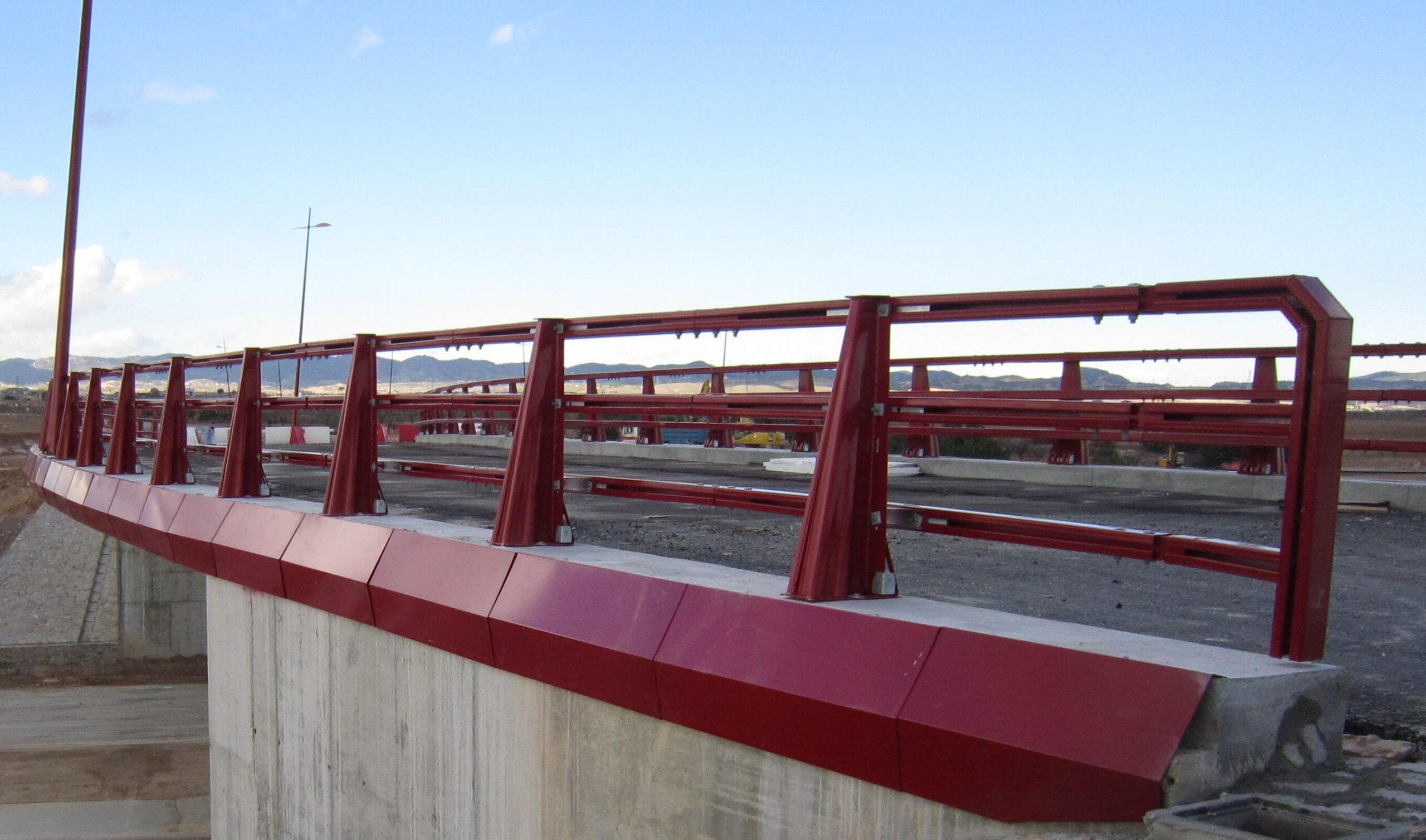
Metal bridge fascias
A metal fascia for bridges is an element that finishes off the edge of the bridge deck, either to accommodate electricity, gas or water conduits or for cladding. This type of bridge equipment embellishes the bridge, not only providing functionality, but also elegance.

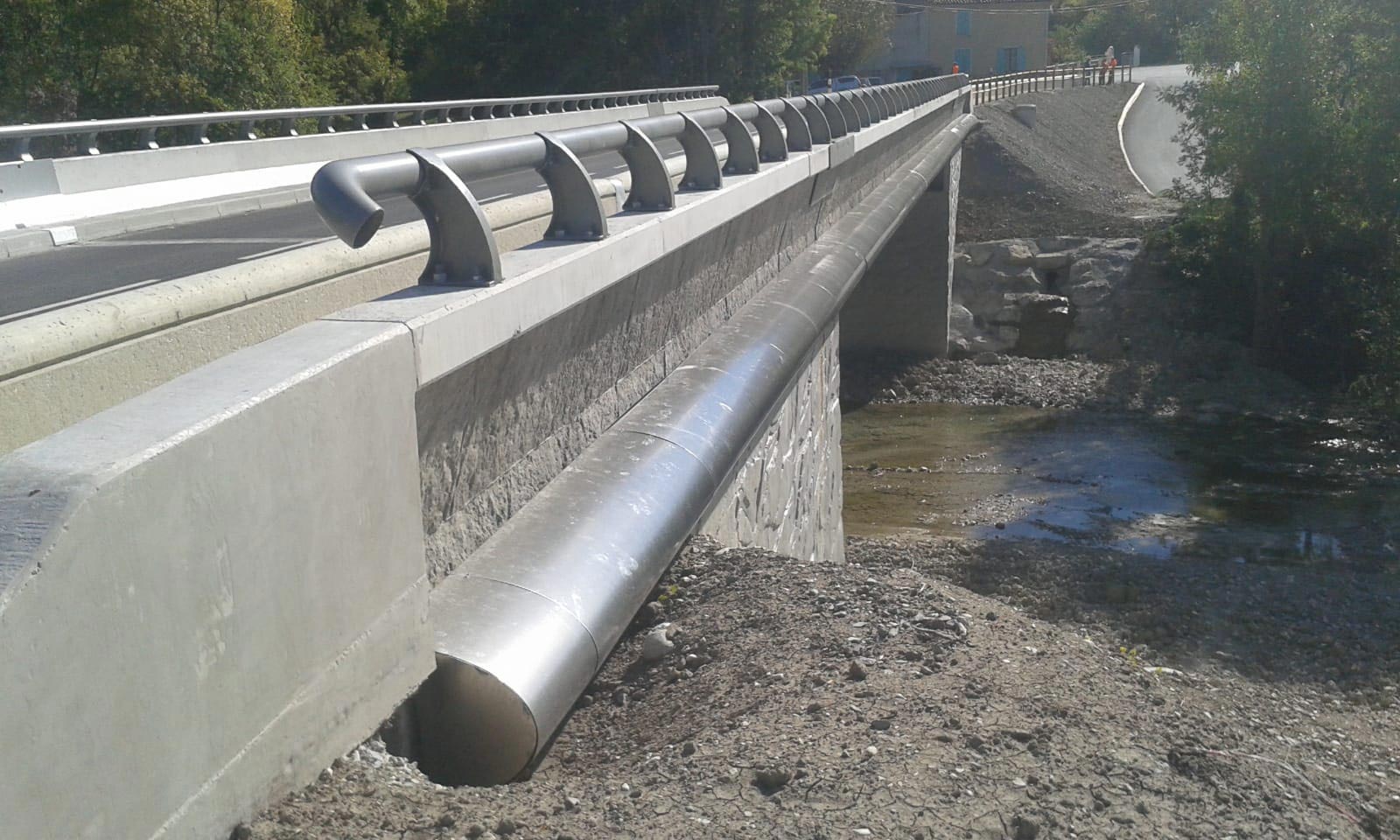
Cornices for bridges
Like fascias, cornices for bridges are a type of equipment for bridges that also reinforces the structure by providing greater rigidity, and allows housing to accommodate electricity, gas or water conduits. They are very common in France.

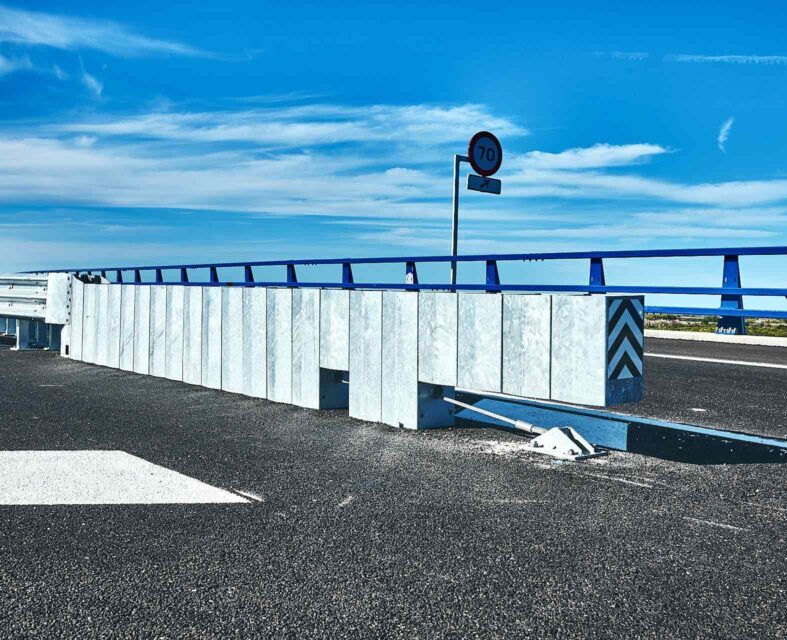
Crash cushions
Crash cushions are considered one of the most effective life-saving devices. They consist of a deformable structure that brakes the vehicle in the event of a crash, absorbing the impact, considerably reducing the serious consequences of the accident.
At Metalesa we have a wide variety of models, which is essential to place them in the correct position on the road so that they can fulfill their function. Each model is suitable to withstand different energy levels depending on the weight and type of vehicle and the impact speed. In addition, these are approved according to the UNE EN 1317-3 standard, which defines the test conditions for obtaining the CE marking.

This Christmas, we are going to accompany you on all your trips. We want to protect you and that your destiny is none other than to meet those you love so much. Our products on the roads save lives, but never let your guard down because Road Safety does not understand holidays. Protection is our goal!
Crash Cushions and Barrier Terminals. Application criteria
Vehicle Containment Systems (VCS) are undoubtedly one of the key elements when it comes to measuring the level of road safety on our road network. These systems, if installed with the appropriate quality standards, significantly reduce the consequences of accidents, mainly off-road or frontal impacts.
There are many national and international regulations that allow the evaluation and certification of products, and that establish a guide of criteria to install them properly, always according to the characteristics of the road and the prescriptions of its manufacturer.
Regulations for vehicle containment systems
The applicable regulation in Europe is UNE EN 1317, which includes several parts with which to evaluate barriers, parapets, crash cushions, transitions between VCS, barrier terminals, removable barrier sections, as well as motorcyclist protection systems. Once established throughout the common European area, each administration must transpose these guidelines by adding its own local criteria. In the case of the Spanish administration, installation criteria for vehicle containment systems is defined in the 35/2014 Circular Order.
This regulation applies in the National Roads Network establishing installation criteria mainly for both barriers and bridge parapets. However, if you are looking for installation criteria for crash cushions or terminals, you will hardly find any reference in article 6.6 where terminals are mentioned as barrier ends, in articles 6.7.3 and 6.7.4 where their differences are mixed, and finally, in article 9, where they are once again mixed up without clarifying when to use one or the other.
Crash cushions have CE marking because part 3 of EN 1317 is harmonized by part 5. However, the terminals do not have CE marking as they are not harmonized by that part 5.
Terminal and Impact Attenuator Performance Levels
Additionally, these systems are classified according to their level of behaviour:
- The Crash Cushions can be of classified as Behaviour Level 50, 80, 100 and 110. This number refers to the speed at which they are tested. For each level, the standard provides for 5 full-scale tests with different directions and angles of approach.

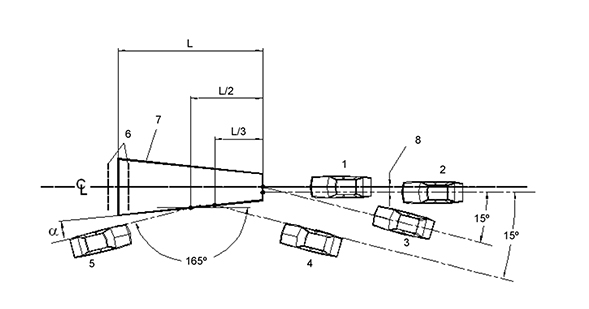
- The Barrier Terminals are currently classified by their Class of Behaviour P1, P2, P3 and P4 according to part 4 of the standard. This part 4 is valid, but it is expected to be imminently replaced by a new Technical Specification for Barrier Terminals recently approved by the Standardization Committee. In this TS, the Terminals are classified differently, as T50, T80, T100 and T110, which is a very similar classification to that of the crash cushions. As for the full-scale tests, up to 6 tests are contemplated to evaluate their behaviour.
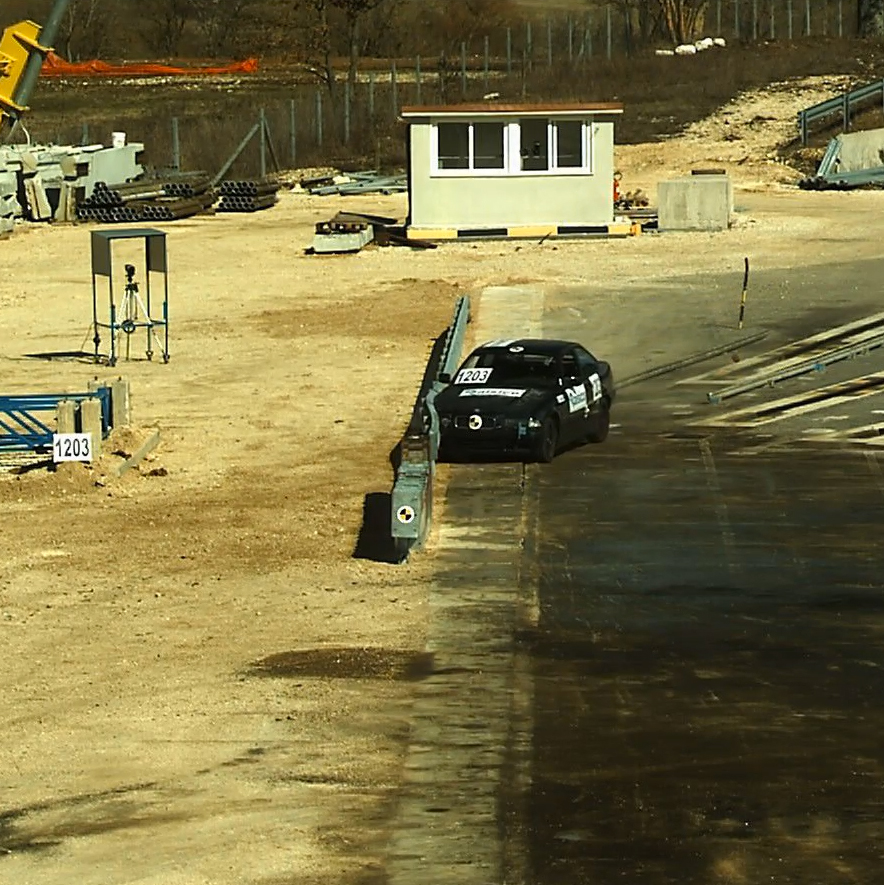

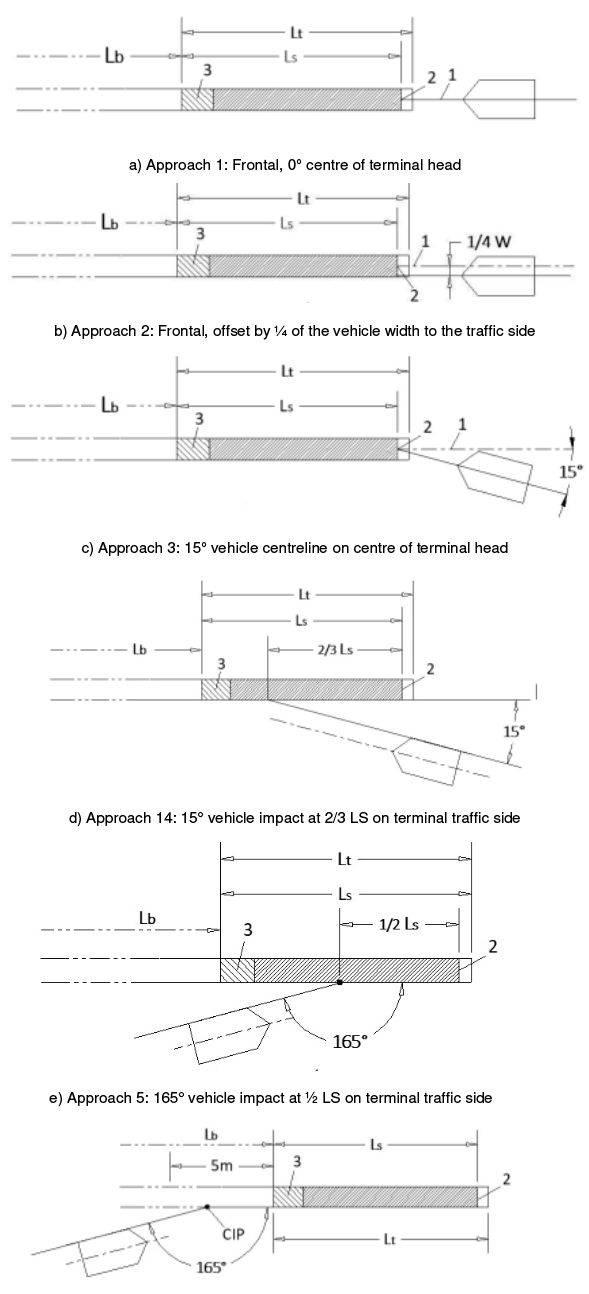
All these tests make it possible to characterize the crash cushions and barrier terminals, assigning them deformation parameters associated with the displacements that have occurred in the test itself, as well as severity values for the vehicle occupants.
Criteria for application of Crash Cushions and Barrier Terminals
As seen, the European regulations brings some light to these road safety systems, but when it comes to the actual project on site, where the variety of scenarios is very wide, OC 35/2014 lacks criteria about when using terminals and/or crash cushions, compared to the exhaustive detail of barriers and parapets. For example, in the case of barriers and bridge parapets we can define what level of behaviour is required depending on the severity of the accident and the characteristics of the road. However, in the case of terminals and crash cushions there is no common criteria that guides the choice of the system. One option is to choose the system based on the speed of the track and the speed at which the system was tested. Curiously, this criterion is not the one applied to barriers or bridge parapets, where it is common to install a parapet tested at 70 km/h on a road where driving at 120 km/h is allowed.
Another common point of installation of barrier terminals and crash cushions is in divergences. Once again, the OC lacks installation criteria in these locations, a problem that raises many questions. For example, which road branch to prioritize and whether or not the shoulders of both branches have to be respected, or, for example, the position of the system on the crossroads, more or less away from the vertex of the divergence. In this case, it will be necessary to assess how much barriers of both branches can converge.
This positioning variability affects the chosen solution, since the crash cushions and barrier terminals can be obtained in families where, for the same system, there are several solutions in terms of widths and even inclinations of the walls, from 300mm to 2300mm wide.
These very brief notes regarding application criteria barely cover a few of the many doubtful aspects that are dealt with in much greater detail in a 40-minute webinar where, with many examples, photos and videos, we try to shed some light on the criteria that we are currently applying, To see this webinar access here.
Range of Impact Attenuators with CE marking from METALESA
By way of conclusion, we would like to point out that private companies are systematically developing new and better systems that optimize road safety conditions on our roads. But none of these will not go very far if it is not led by legal and regulatory tools that define how to use VCS efficiently and homogeneously. At Metalesa we have extensive experience in application criteria for these systems after multiple projects, and in case of doubt, we will be happy to advise and guide any technician and professional to shed some light on this world of vehicle containment systems.
Know the regulations of containment systems
At Metalesa, whenever we talk to you about our products, we tell you what they are for, all their features, their advantages... That is why today we bring you a slightly different article in which we will talk about a topic that we usually touch on on our blog: regulation of vehicle containment systems UNE EN 1317.
If you need to review the existing vehicle containment systems, we recommend you read this article by clicking on this link.
A common regulation for the improvement of Road Safety
Since January 2011, it is mandatory for vehicle restraint systems installed in the European Union to be certified under the UNE EN 1317 standard. The creation of this standard implies the homogenization of the testing methodology for restraint systems and acceptance criteria, thus favoring Road Safety.
We understand that such technical standards can be difficult to understand and interpret, therefore, at Metalesa, as experts in the UNE EN 1317 Standard and as part of the UNE CTN135 standardization committee, we want to be your reference in Containment Systems Regulations . For this reason, in this article we will explain everything you need to know about the UNE 1317 Standard.
What is the UNE?
To explain the UNE EN 1317 regulation, it is first important to know where it comes from.
The UNE (Spanish Association for Standardization) is the only Standardization Organization in Spain. Its work lies in the creation of regulations for the different sectors, so that they conform to a series of standardized and accepted norms, which guarantee the quality and excellence of companies.
Specifically, at Metalesa we are part of the CTN-135 Standardization Committee (Equipment for Road Signalling), which is responsible for developing standards for the standardization of those elements or equipment intended for signalling, security, beaconing and traffic intended for information, planning and road safety. Therefore, the creation of standards related to vehicle restraint systems is included here.
Since its creation, the CTN-135 Normalizing Committee has elaborated 283 norms to favour Road Safety. In this article, we will focus specifically on the UNE EN 1317 standard.

Everything you need to know about the UNE EN 1317 STANDARD, the regulations for Vehicle Containment Systems
Vehicle restraint systems are essential Road Safety equipment on roads to avoid the serious consequences of an accident, which is why it is so important that their operation is subject to the acceptance criteria imposed by the UNE EN 1317 standard.
These are the factors it takes into account:
- Containment level: Ensures that the containment system contains the vehicle in the event of a crash, without overturning the car or passing through the system.
- Impact Severity: Reduces decelerations to minimize damage to vehicle occupants.
- System deformation: Refers to the transverse displacement of the system during impact.
- Redirection: Ensures the return to the road in a controlled manner of the vehicle that hits the containment system, in such a way that it does not invade other lanes.

Taking into account the above variables, we can differentiate between different types of restraint systems that differ in the consequences and effects that the impact of the vehicle has on the vehicle, the occupants, and the restraint system itself.
All containment systems are subjected to full-scale tests in which the above criteria are taken into account and must be passed in order to comply with the UNE EN 1317 standard.
Next, we are going to explain in a more extensive way each of the parameters that characterize containment systems:
Containment Level
It refers to the capacity of a Restraint System to withstand the impact load of a vehicle.
The risk of accidents on a given road, the speed allowed and the average number of heavy vehicles in each direction at the time of commissioning, determine the choice of the level of containment that a vehicle containment barrier must have.
In this sense, the UNE EN 1317 standard defines several containment levels, which are accepted when they pass rigorous full-scale tests. The list of essays that accredit each level can be seen in this image:
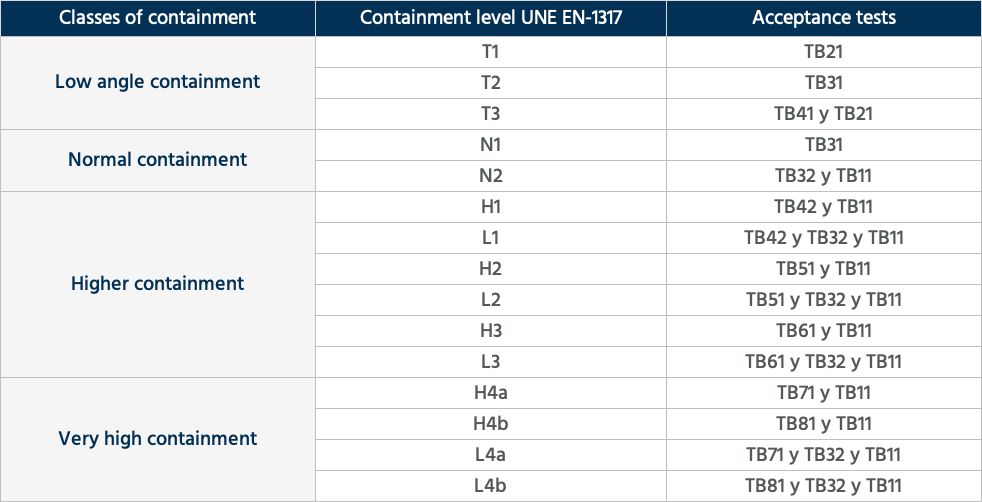
These full-scale tests are carried out in accredited laboratories, so that values are set for the speed at the moment of the crash, for the mass of the vehicle, and the angle at which it hits the vehicle restraint system.

Once the containment level has been established, a complex system of high-performance cameras and sensors calibrated in the laboratory allow the behaviour of a containment system to be defined by means of specific values of the following parameters.
Impact Severity Level
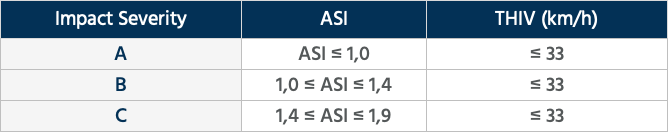
The collision of a vehicle against a restraint system entails risks for its occupants. The impact severity level is defined by the severity of the risks inside the vehicle.
The Impact Safety level is calculated from the combination of the following values: Head Impact (THIV) and Deceleration (ASI).
It is important to note that, in Europe, the installation of an impact severity C restraint system is not authorised, as this value may involve a fatal impact for the driver of the vehicle.
System Deformation
The behavior of a safety barrier is characterized by the transverse displacement of the system at the moment of impact. This is defined in the full-scale tests through the working width and dynamic deflection parameters.
- Dynamic Deflection: Refers to the maximum lateral dynamic displacement of the face of the Vehicle Restraint System closest to the traffic on the road. It is measured in meters.
- Working Width: It is the distance between the face of the containment barrier closest to the flow of traffic before the impact occurs, and the farthest lateral position that during the impact reaches any essential part of the safety device. . The standard classifies this parameter from W1 to W8 depending on the meters of displacement.
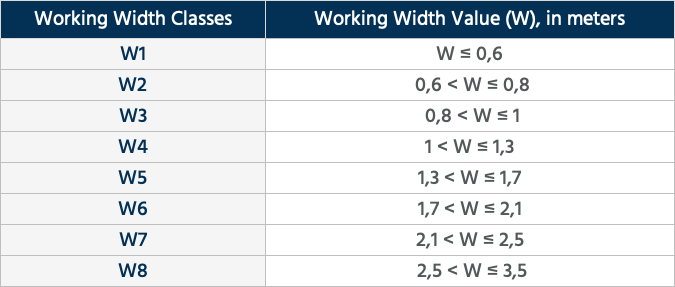
- Vehicle intrusion: This is the maximum dynamic lateral displacement of the containment system facing traffic without deforming. This parameter is evaluated through high-speed photographic or video recordings, considering a hypothetical load of length and width equal to that of the vehicle platform, and a total height of 4m. The UNE EN 1317 standard classifies this parameter from VI5 to VI5, depending on the meters of displacement.
Taking into account the above variables, we can characterize the various types of restraint systems, which will differ in the consequences and effects that the impact of the vehicle has on the vehicle, the occupants, and the restraint system itself.
We remind you that all containment systems with CE marking have been subjected to full-scale tests in which these criteria have been taken into account.
At Metalesa we are in charge of designing, manufacturing and installing vehicle containment systems taking into account all the acceptance criteria dictated by the UNE EN 1317 standard. In this way, we can guarantee the protection of people, and for this reason we must understand the regulations to perfection.
If after reading this article you still have any questions to resolve regarding the UNE EN 1317 regulation, we recommend you take a look at our section of frequently asked questions about containment systems, or if you prefer, you can contact us directly, we will be happy to answer your query.
Discover our range of containment systems to improve Road Safety
Ensuring road safety is everyone's responsibility. Drivers should be aware that each journey by car can have serious consequences if they are not driven carefully, but it is also necessary that the public authorities that manage transport infrastructures guarantee safe roads to minimize the severity of accidents as much as possible. This is something that is already being done by both parties: drivers are increasingly responsible behind the wheel and the authorities are working to build safe roads. Proof of this are the results of the latest report from the European Transport Safety Council (ETSC), which indicates that between 2001 and 2020 the accident rate on Spanish roads fell from 5,517 victims to 1,370. That is, 75.2% less. These figures position Spain as the country in Europe in which deaths in traffic accidents have fallen the most during this century. In this sense, Road Safety studies and improvement of the most conflictive points are absolutely essential to progressively improve the road network. One of the most important elements of your safety equipment is containment systems.
Infrastructures for Road Safety: Vehicle containment systems
What is a containment system?
Vehicle restraint systems are safety barriers located on the roads to mitigate the consequences of accidents due to exits.
Road exits make up between 35% and 40% of road accidents. Given these high percentages, it is convenient to ask ourselves what type of containment systems it is necessary to install on those roads with a high risk of accidents. Said vehicle containment systems ‘act’ in various situations such as:
- When the vehicle leaves the road in an uncontrolled way.
- When there is a risk of falling down steep slopes.
- When the vehicle invades another lane.
- When there are obstacles on the road with which the vehicle can impact.
In these types of situations, the absence of containment systems is very likely to lead to a fatal outcome, which is why their installation is so important.
Factors to take into account for the installation of Vehicle Containment Systems
The following factors must be considered in deciding in which situations it will be necessary to install vehicle restraint systems:
- Type of road: If it is a conventional road, highway or highway.
- Characteristics of the section: If it is a curve or a straight section.
- Traffic intensity and composition: This factor refers to the number of each type of vehicle that circulates on the section in question.
- Existing risks on the road: Obstacles, steep slopes, that there are other roads that could be invaded ...
- Distance between road hazards.
After analyzing these factors, it will be decided whether a vehicle restraint system should be installed in the section to mitigate the consequences of accidents. If the study of these factors indicates the need for its installation, the next step is to decide what type of vehicle containment system is required, for which the following parameters are met:
- Containment level: Refers to the capacity of the containment system to retain the vehicle in the event of a collision, redirecting it to the road in stable conditions, that is, the vehicle does not overturn or the containment system does not penetrate inside.
- Impact severity: The risk of the occupants when the vehicle collides in front of the restraint system.
- System deformation: The measurement of the degree of deformation of the containment system when the impact occurs, serves to define the distance at which said infrastructure has to be installed with respect to the dangerous area or obstacle.
- Redirection capacity: Ability of the vehicle restraint system to change the trajectory of the passenger car when the crash occurs, allowing the exit to be as parallel as possible to the direction of traffic.
Types of Metal Vehicle Containment Systems
After carrying out the previous analysis, we will proceed to select the most suitable containment system. At Metalesa, we are experts in the design, manufacture and installation of vehicle restraint systems and we have a wide range that allows us to adapt to all existing situations in terms of Road Safety.
Steel Bridge Parapet META13
This type of vehicle containment system is installed on the edges of bridge decks, supporting wall crowns, passage works… It is a H2 level containment system.
Some of the main advantages of the Steel Bridge Parapet META13 are the flexibility of the containment system, its fusible anchoring system that allows a simple and quick replacement in the event of a crash, and its versatility, since it allows it to function as a vehicle containment system. and pedestrians installing a grid.
It is a device approved according to the UNE EN 1317 parts 1 and 2 standard, which together with compliance with part 5 in terms of production control, has obtained the CE marking.
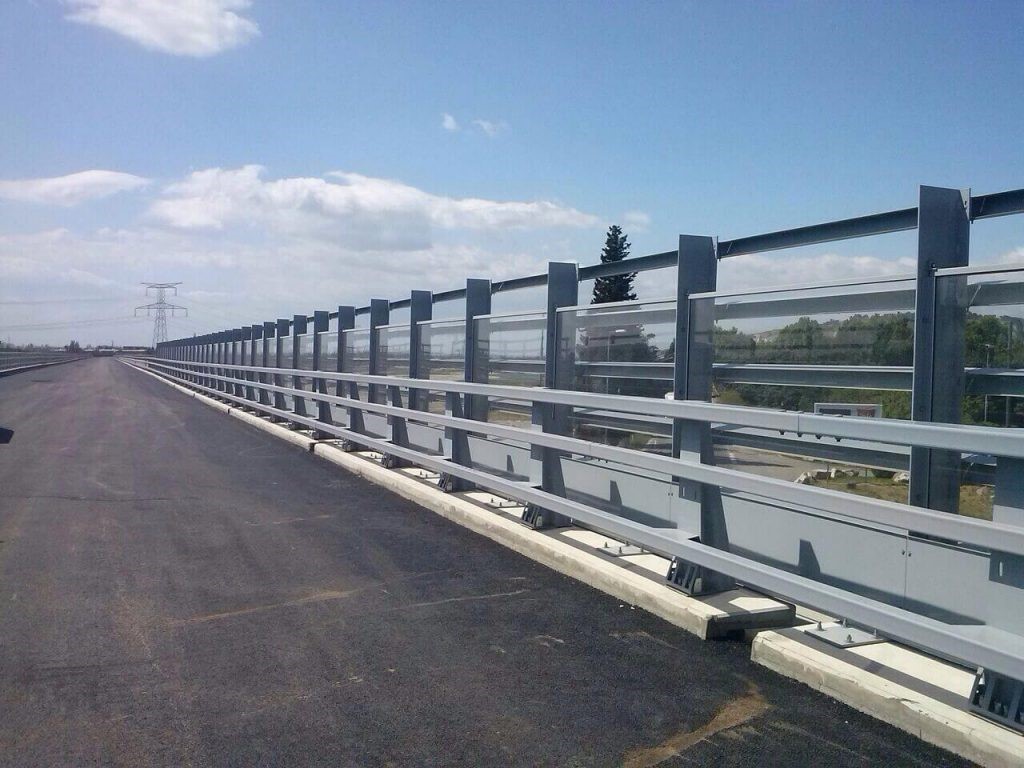

Steel Bridge Parapet META16
The Steel Bridge Parapet META16 is our H3 containment system, which also has the CE marking after passing rigorous full-scale laboratory tests.
Some of the advantages of this vehicle restraint system are the following: It is light and of small dimensions, it allows the installation of vandal-proof fences and the placement of acoustic screens at a very short distance from the parapet, and due to its reduced number of components the assembly it's simple.
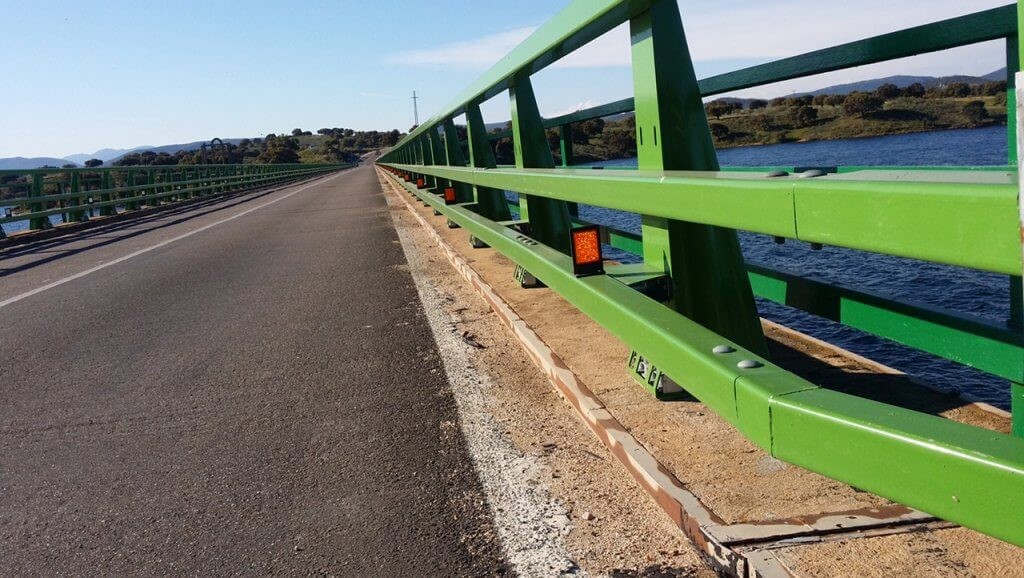

Impact End Terminals
Impact End Terminals are equipment that is characterized in that they are always attached to the end of a vehicle restraint system. They cannot be installed autonomously.
We have several models tested in accordance with the European standard prEN 1317-7, all of which provide the flexibility of joining with double or triple wave bionds, or with normal or double bionds (on both sides).

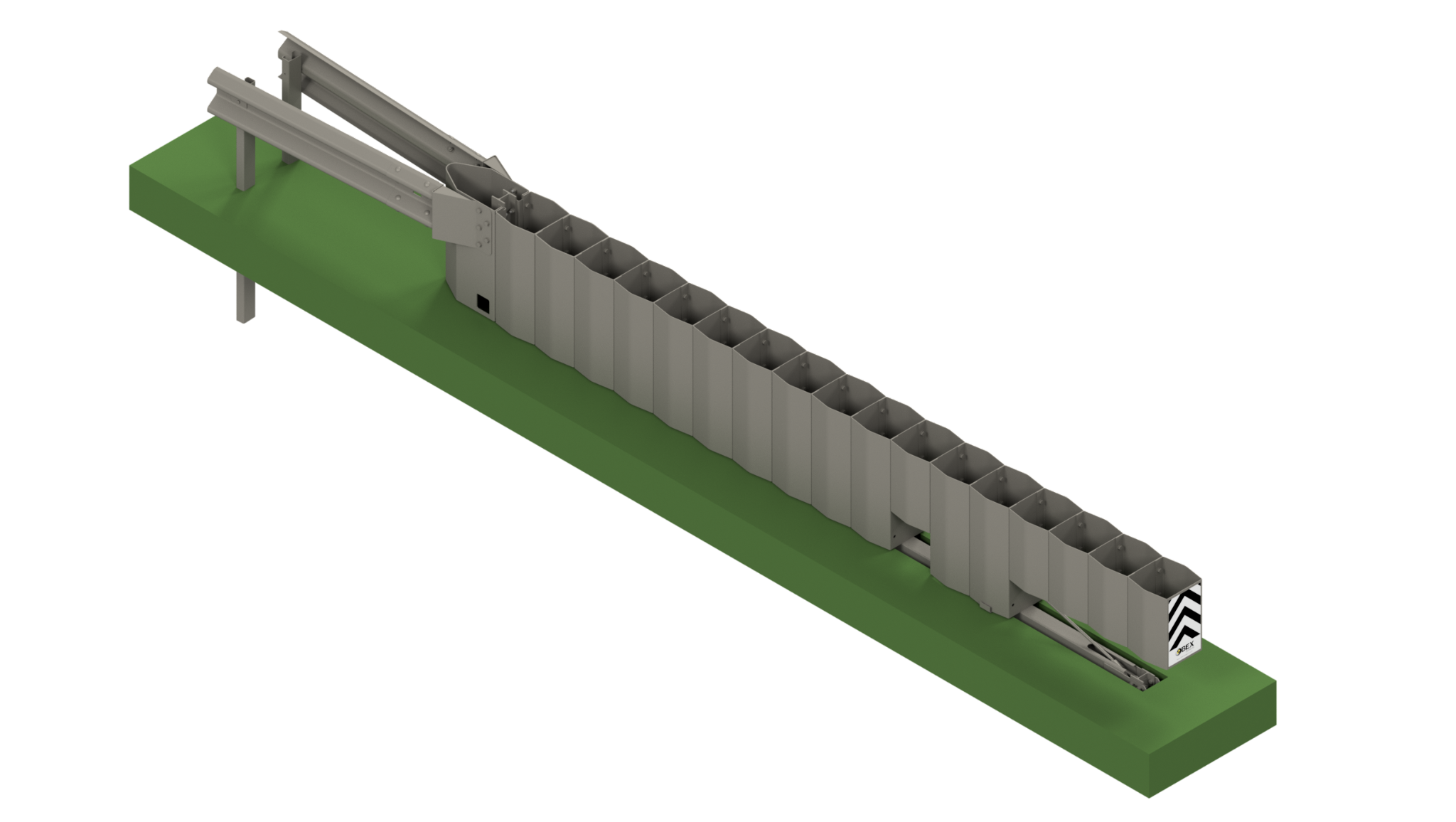
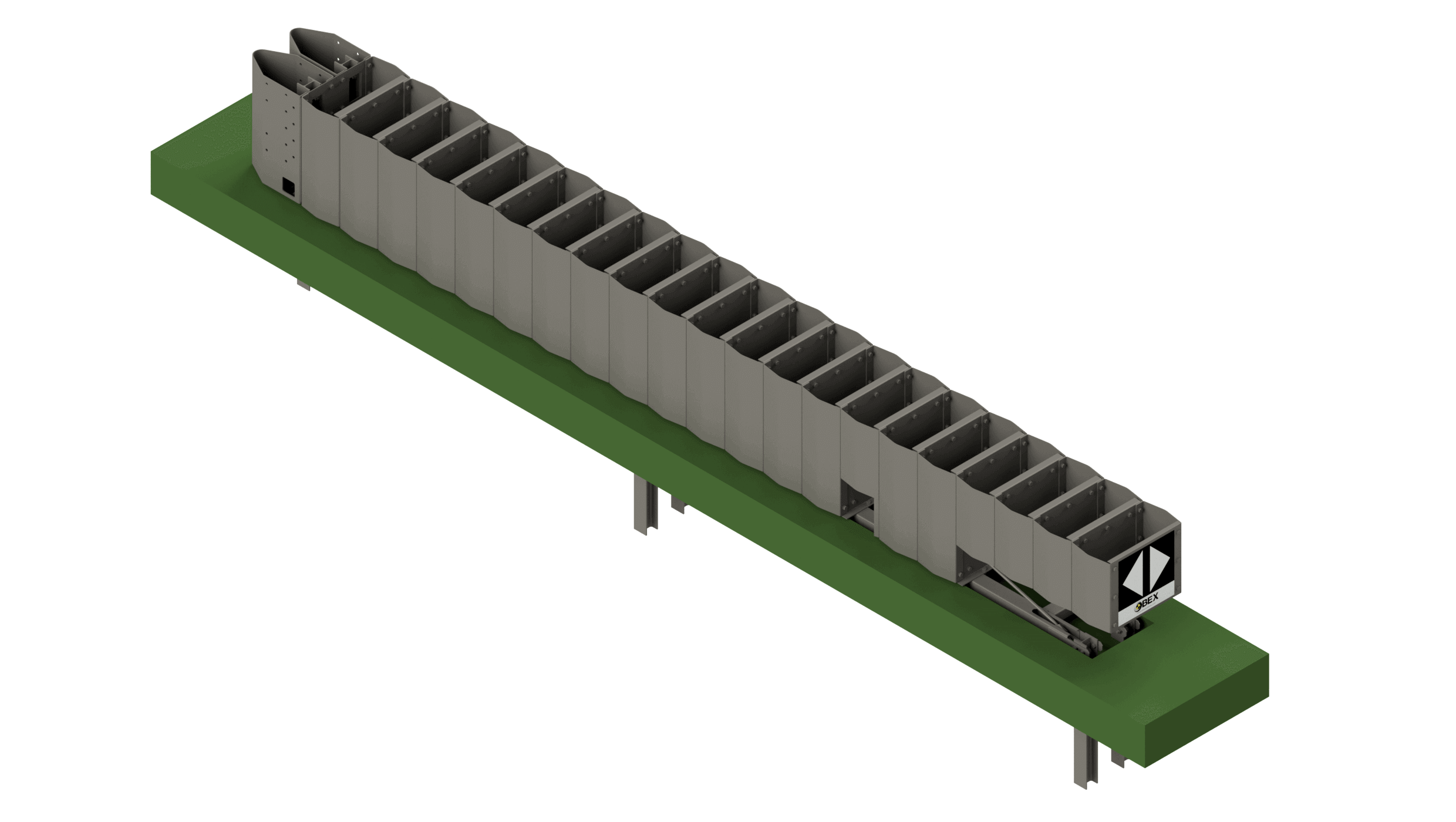
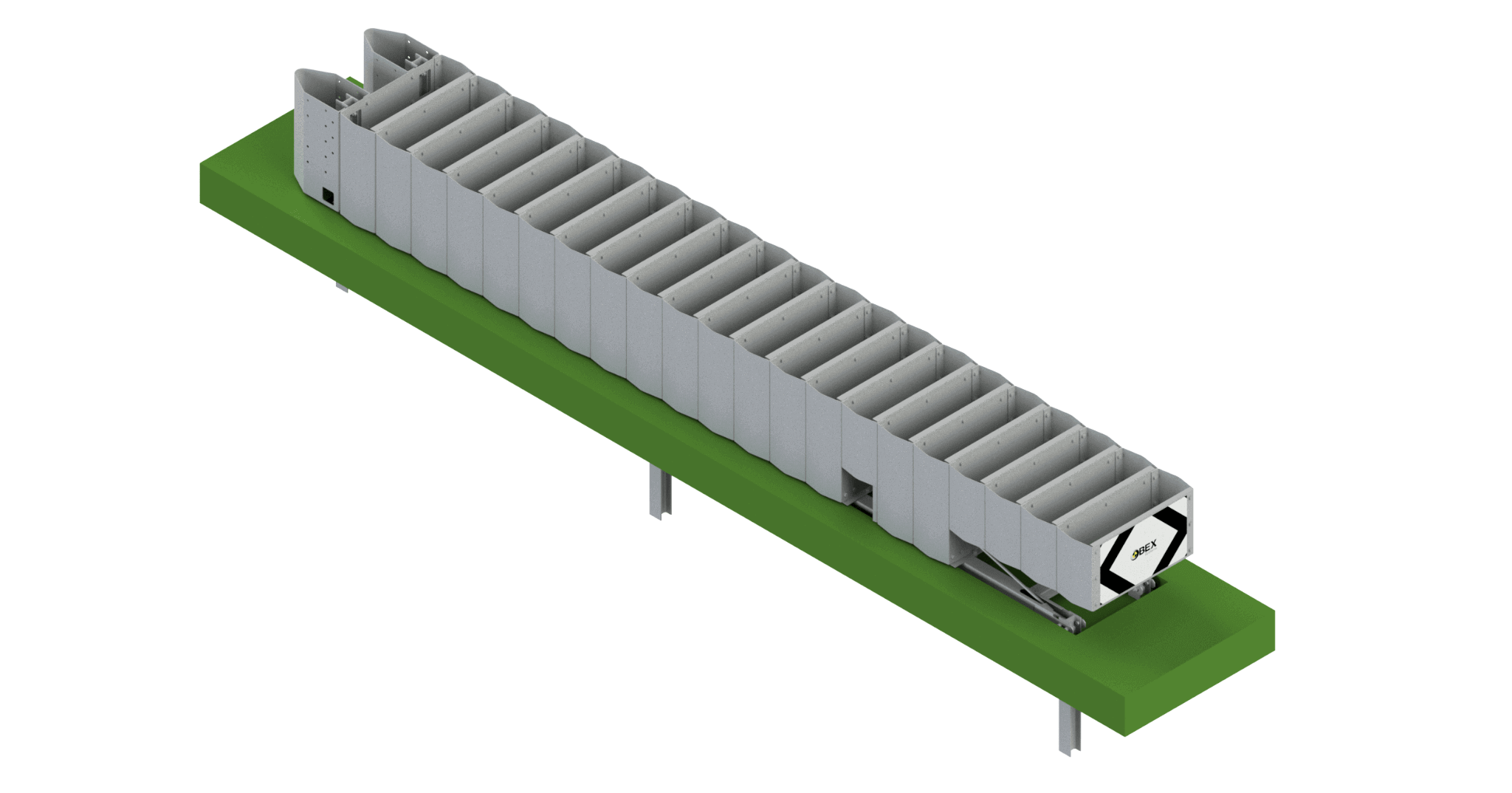
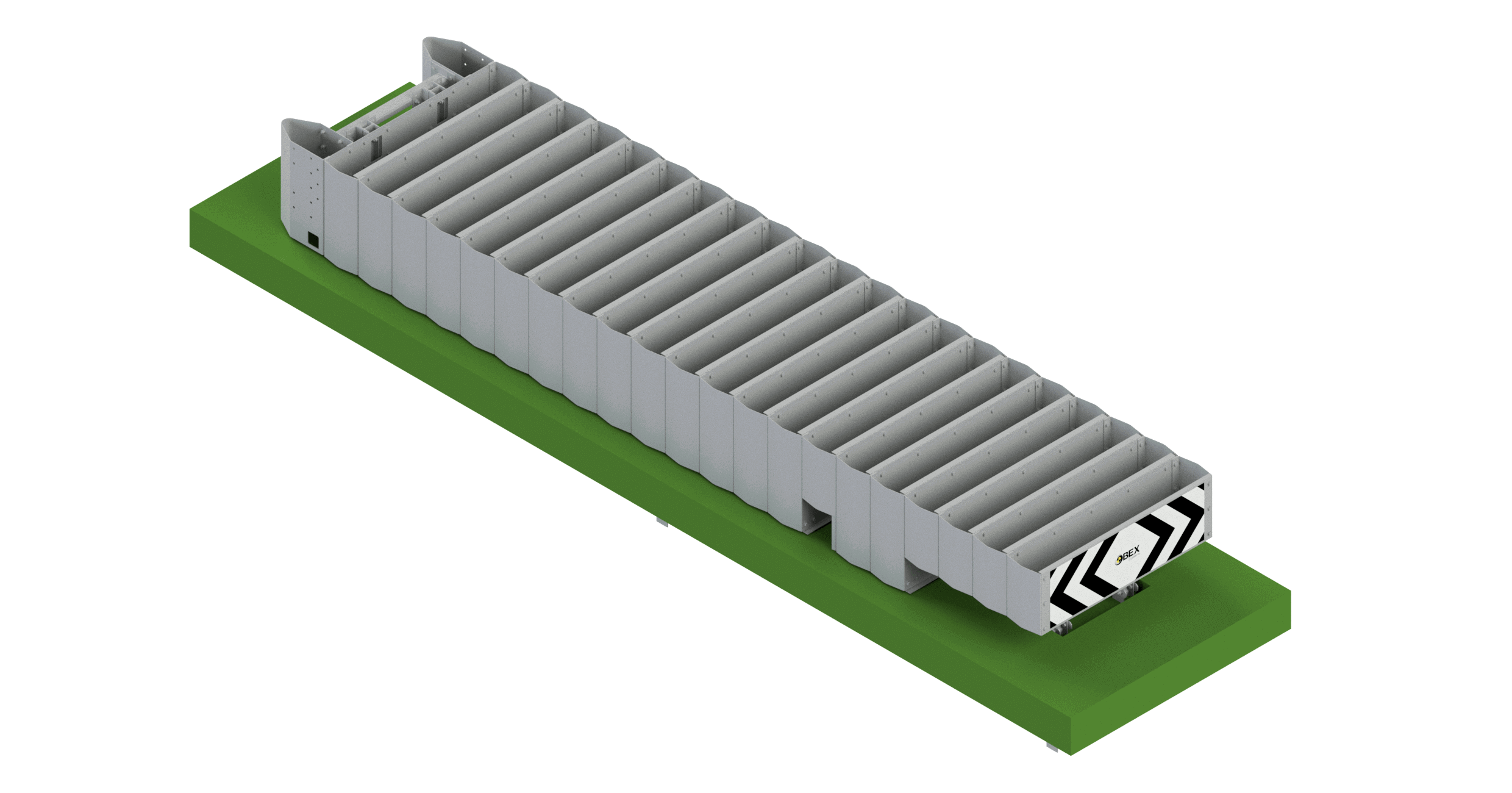
Crash Cushions
A Crash cushion or shock absorber is a vehicle restraint system that absorbs frontal or side impacts without the risk of intrusion of components in the vehicle compartment, being its installation more and more frequent since it allows to significantly reduce the victims in accidents.
We have a wide variety of models that can be installed on concrete slab or directly on the ground. In case of impact, the infrastructure is easy to repair or replace.
Mixed Parapet PXP
It is a mixed vehicle containment system, as it is made up of a concrete parapet and a metal railing. The latter is installed on the concrete parapet, which guarantees a better containment system against the collision of a heavy vehicle.
In addition, its aesthetics provide excellent integration on the tracks, it is easy to install and we have several models of handrails: With a through tube to a ring welded to each support, with a tube welded directly to each support, or other models according to installation conditions.

At Metalesa we are aware that our products save lives, and that is why we have a great responsibility. In this sense, it is not only important that the authorities worry about the installation of containment systems on the roads, but also to ensure that these infrastructures are of quality, there is a lot at stake. From Metalesa we can guarantee that quality in our products to ensure safe roads.
If you want to obtain a quote for the installation of our vehicle containment systems, call us at +34 96 088 99 44 or send us an email to metalesa@metalesa.com
This summer, Road Safety on the roads
The time most desired by most has finally arrived, the summer holidays. Heat, beach, disconnection from work and the daily routine ... Unfortunately, the other side of the coin is the usual increase in traffic accidents due to the enormous volume of vehicles moving on the roads.
In addition, this year we are facing a somewhat different summer, as we come from a time marked by mobility restrictions and the health emergency due to COVID-19. For a long time we have had to stay in our regions without the possibility of vacations or travel, so it is natural that with the arrival of good weather there is a significant increase in national travel, and with the need to be extremely careful on the roads.
Road Safety is everyone's business. If we are all aware of the importance of being responsible when driving, we will be able to minimize the risk of serious accidents.

Increased risks on the roads in summer
In addition to the characteristic increase in summer traffic, there are other typical summer factors that pose an added risk on the roads and that must be taken into account.
Caution with heat
In Spain, on the hottest days of summer, the temperature of a car exposed to the sun for a long period of time can exceed 50 degrees, which is a risk when driving. For this reason, before getting in the car and starting the trip, it is recommended to ventilate it by opening windows and doors, turning on the air conditioning and not starting the trip until the interior of the vehicle has acclimatized. If possible, the ideal is to avoid driving in the hottest hours of the day.
Take care of your hydratation and never drink alcohol
Lack of hydration can lead to serious risks while driving. The most common symptoms of dehydration are usually fatigue and drowsiness ... It is recommended not to wait to experience these signs to drink water. Always keep a bottle of water on hand in your vehicle and drink frequently, even if you don't feel particularly thirsty.
It's also a no-brainer, and hundreds of drivers are penalized every day for exceeding the permitted alcohol level behind the wheel. Do not drink and drive!
Food before and during your trip
If we are going to take long trips in summer, it is important to eat light meals. Otherwise, digestive discomfort can occur that can distract us from driving and affect Road Safety, and also cause drowsiness.
Always travel with suitable and comfortable cloting
Beyond driving in loose fitting, comfortable clothing, it is especially important to note that flip flops should not be worn. The risks of driving with this type of footwear are very serious: they can get caught between the pedals, slip ... and prevent reacting in time in the event of an accident.
That sunglasses are never missing
Lack of vision can be one of the main reasons for accident risk. Therefore, it is advisable to wear polarized sunglasses to avoid glare and prevent eye fatigue.
Check your vehicle before and during the journey
It is important to thoroughly check the vehicle before any trip, and especially if it is a long journey. Tires, brakes, check the oil level, the coolant level, check that the lighting devices are working, make sure that the air filter is clean and always wear vests and safety triangles.
Calculate your route previously
Improvisation can be part of the unforgettable trip, but in driving it is not recommended. The ideal is to plan the route to your destination in advance, take into account the stops to rest ... In addition, this way you will avoid being constantly aware of the GPS and you will pay more attention to the road. And of course, the use of mobile phones while driving, unless it is to use it as a passive GPS, is totally prohibited.
Always control your speed
We know, controlling speeding is something very obvious when we go on a trip. But still every day traffic accidents happen precisely due to speeding. Remember, no matter how expert you are at the wheel, extreme caution on the road is a great responsibility that we must all carry out.
Travel accompanied
It is always important to ensure Road Safety, but the commitment is even greater when we transport more people in our vehicle. The co-pilot has to try not to over-entertain the driver to avoid confusion, and in the case of traveling with children, you have to find ways to entertain them using iPads, reading stories ... And of course, it is mandatory to insist that the occupants use the seat belt.

Now you know the most important points to keep in mind when taking a trip during this summer vacation. Today's article we want to serve as a guide that you can always turn to whenever you are going on a road trip. Even so, it is always advisable to visit the DGT website for any notice or news of interest.
At Metalesa, protection is our goal
Our mission is the protection of people. As experts in Road Safety, our activity consists of designing, manufacturing and installing infrastructures specially designed to guarantee the safety of people.
Products for Road Safety on highways
Parapets
Los pretiles para carreteras son sistemas de contención para puentes. En Metalesa disponemos del pretil metálico META13 y el pretil metálico META16, los cuales han sido homologados por la norma UNE EN 1317.
Highway parapets are restraint systems for bridges. At Metalesa we have the META13 metal parapet and the META16 metal parapet, which have been approved by the UNE EN 1317 standard.
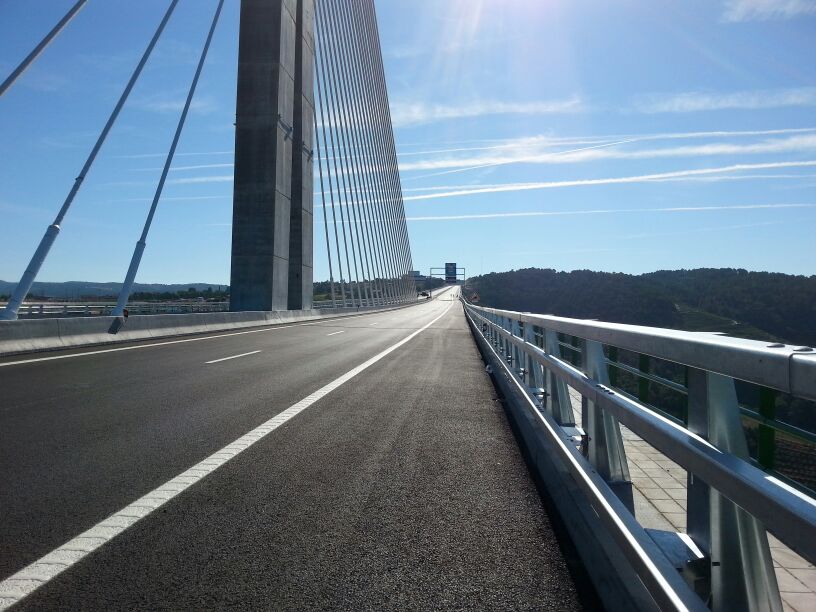

Transitions to concrete barriers
Highway transitions are used to link different vehicle restraint systems, such as a parapet and a concrete barrier. Our transitions are homologated by the French standard NF 058.
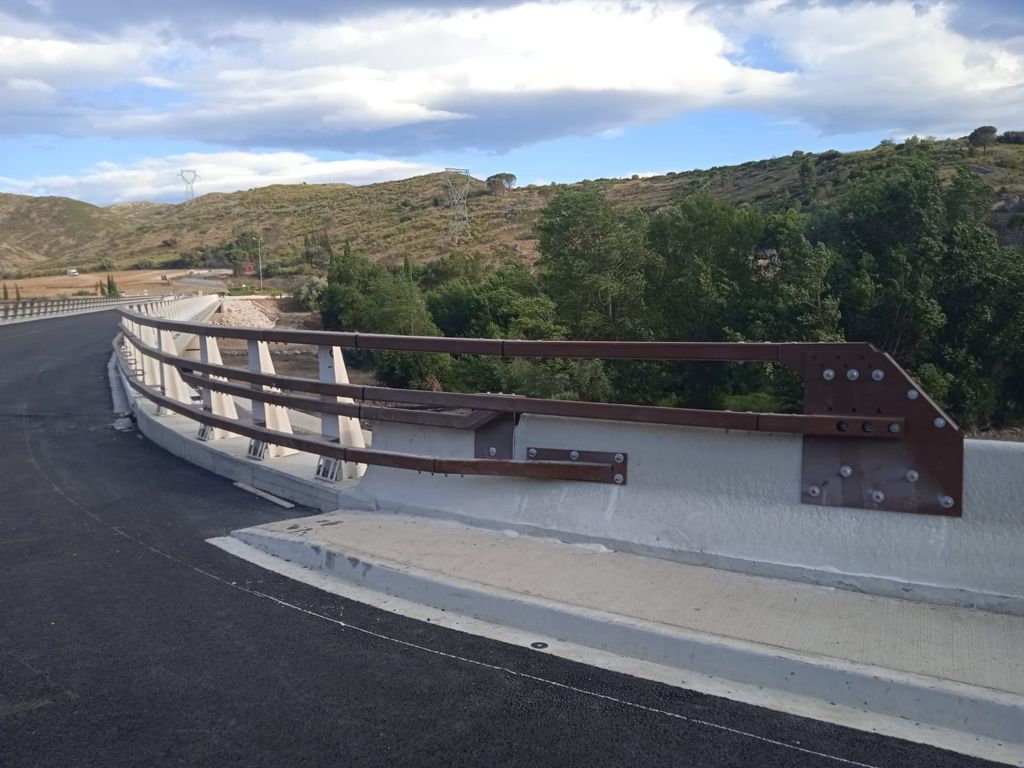

Impact terminals
They are road safety devices that are placed at the ends of the parapets or containment barriers, as a safe ending element. We have several models of impact terminals, which share a series of characteristics such as the possibility of allowing the connection with a double or triple wave bionde, and that all have been tested according to the European standard prEN 1317-7.
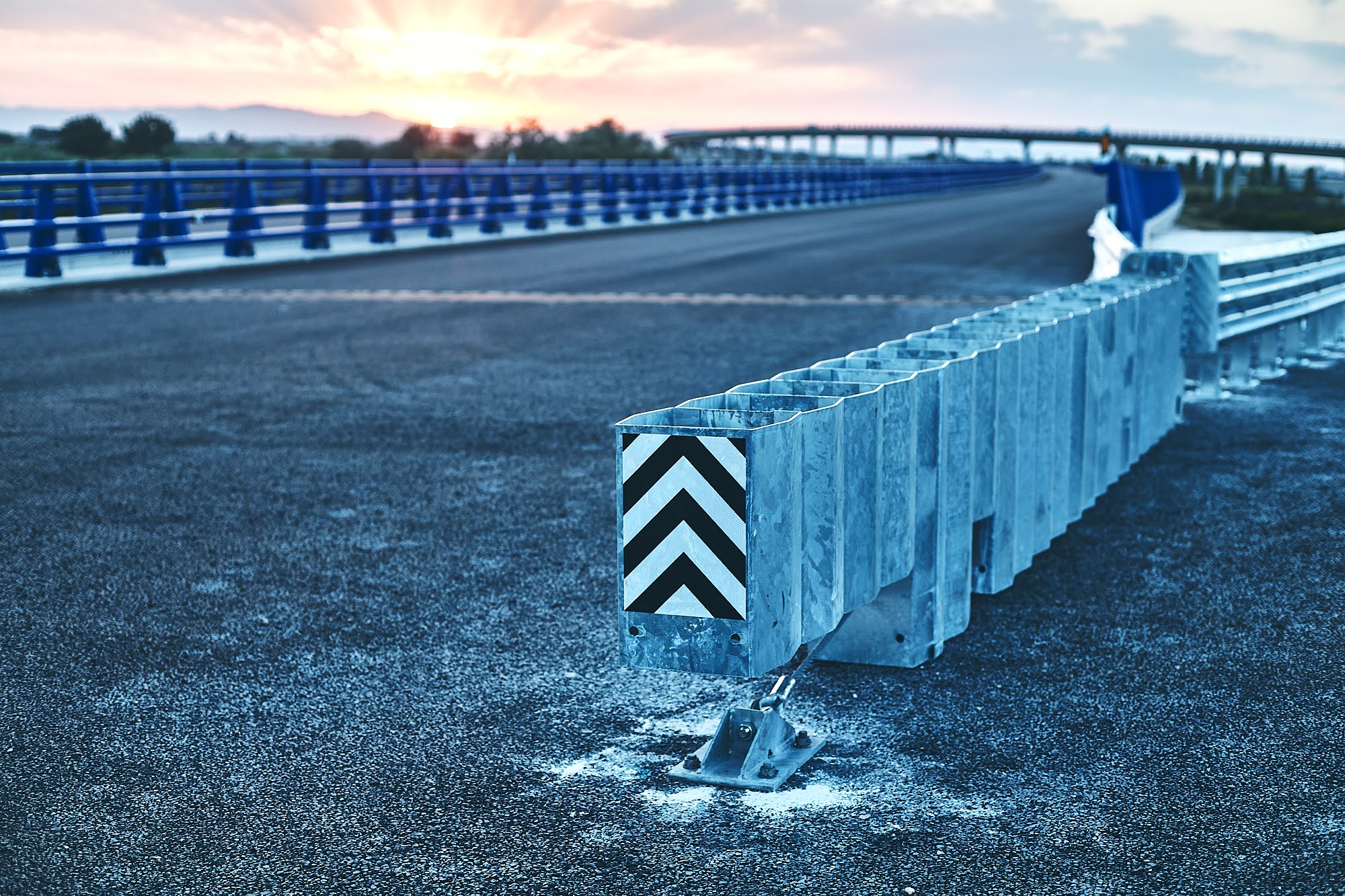

Shock atenuators
Also called shock absorbers, their function is to absorb the impact of the car in the event of a crash. They differ from containment system terminals in that they can be installed in isolation, without being connected to any other system. In addition, in case of impact it is easy to repair.
Having said all this, from Metalesa we want to remember that Security does not go on vacation. Our purpose is to protect society through our products for Road Safety and to educate drivers to have an unforgettable, fun and above all safe vacation. Can you help us achieve this goal?
How has mobility in cities changed?
Mobility through cities is becoming more and more “à la carte” while ways of transport are increasingly modernizing, thus adapting to the needs of different profiles of people. We see how every day companies offer mobility solutions for cities that adapt their services to the comfort and personalization that citizens are demanding, making them more ergonomic, economical and trying to be as respectful as possible with the environment.
The importance of adapting
Currently we want to move faster, save time, and if possible, with the lowest energy consumption and the lowest economic cost. The proliferation of geolocation technology has enabled the use of applications that help us to know real time the arrival of the bus at our stop or how the traffic is in the city. Many cities, in their quest to become smart and sustainable, have established new urban solutions to improve the use of public transport, and have limited traffic in some areas, even prohibiting the circulation of private cars in downtown areas with a high concentration of users.
This trend has materialized in the deployment of solutions such as bollards or bike lanes, the adaptation of all horizontal and vertical signs, and the offer of subsidies for the purchase of personal mobility vehicles. The response of the citizens has not waited long, and thus we have seen massive purchase of bicycles and / or electric scooters, not only in large cities, but also in smaller towns. Little by little, all these measures integratede into comprehensive sustainable urban mobility plans are working together to create pollution-free urban areas.

In a society that is increasingly aware of the importance of caring for the environment, and willing to adapt itself to the new times, it has been inevitable that this type of electric personal mobility is in fashion and that it is expected to continue growing. At the same time, this has acted as a catalyst for the industry to innovate and bring new mobility solutions to market.
This set of chained consequences lead our cities into a virtuous circle that reinforces investment in safe urban mobility, either with solutions such as bollards, or with other types of parapets, guardrails or urban containment barriers. In short, minimizing the risk for pedestrians, cyclists, or those who lean towards the electric scooter.
Our urban mobility solutions
Our commitment to society lays on our purpose of saving lives. This has led Metalesa to work for a long time to improve people's lives. Urban solutions to bring an improved safety for citizens in their daily urban mobility, is a key area where we have been concentrating our efforts in recent years. Some of our most demanded products to improve mobility in cities are urban parapets, cyclopedestrian railings and bollards
- The urban parapet, which Metalesa manufactures and installs, is a containment system designed to be installed on urban roads or with a limitation of up to 20, 30 or 50km/h. Manufactured for its perfect integration in the urban areas such as streets, avenues or roundabouts.
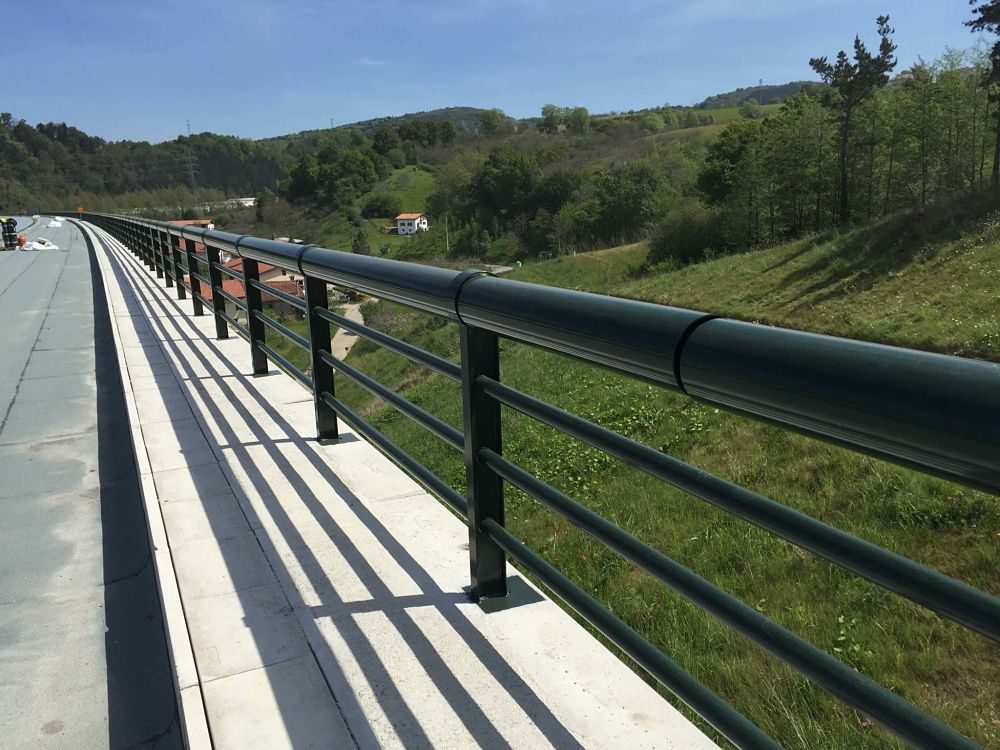

- As for the cyclopedestrian railings, we have a wide variety of models capable of adapting to the road infrastructures of any city. It is an urban containment system in order to protect both pedestrians and cyclists who pass through the bike lane from road traffic.
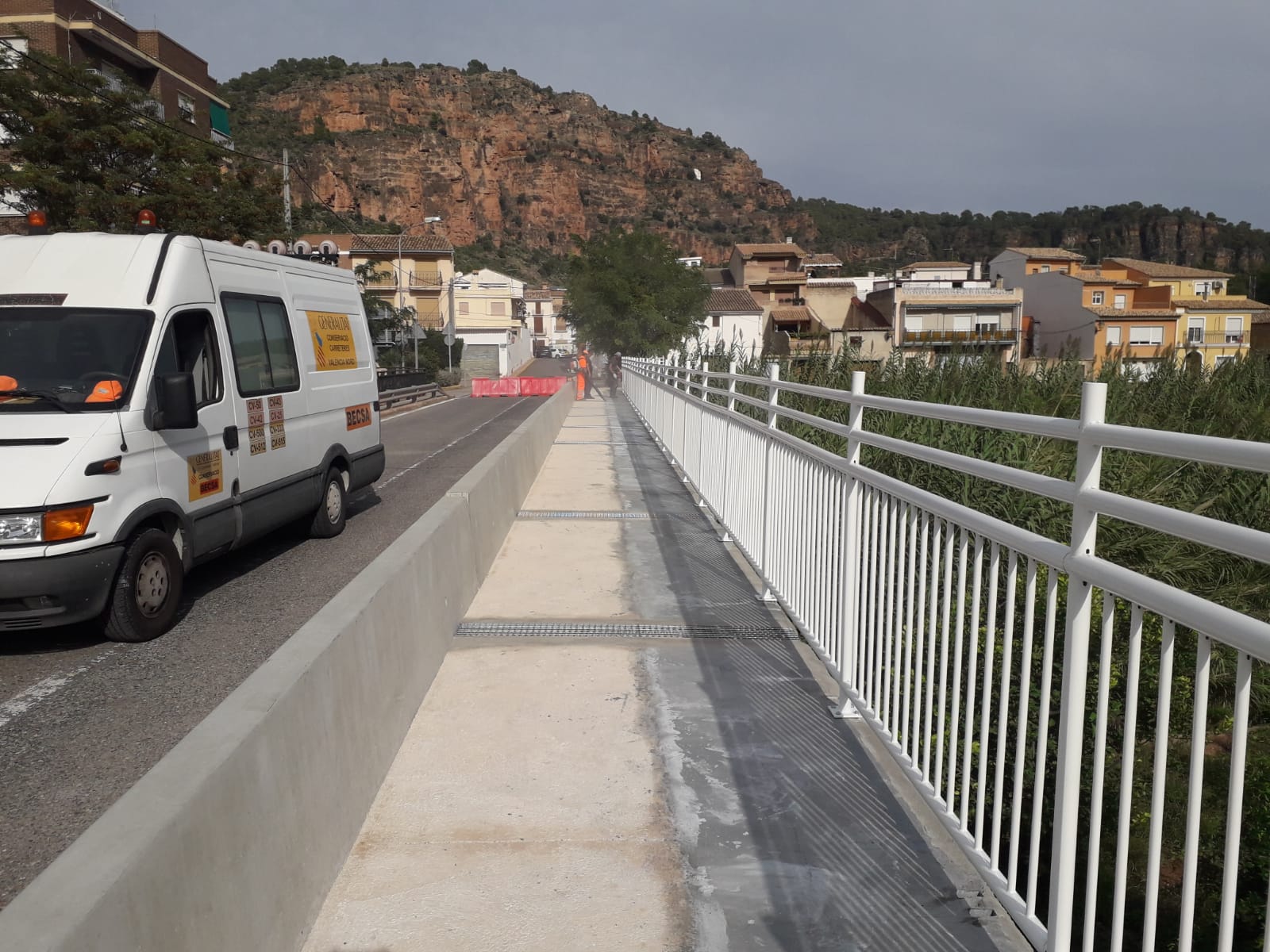

- We also have a wide variety of bollards. Its main objective is to delimit vehicle access to pedestrian, cycling, or leisure areas. To this day, it continues to be a safe bet for the improvement of mobility in cities. We have also carried out a number of installations in private areas of industries or logistics centers.

If you want to put an end to these problems and want a smart solution, don't hesitate to contact us. Our service of technicians and advisers of the commercial department will not hesitate to offer you a proposal that adjusts to your reality so that our service is 100% effective.
Safety in urban areas and on the cycling lanes
As experts in Road Safety, one of our tasks should be to promote greater awareness about the safety of people, both in urban areas and on roads. In this sense, although our products are intended to make people’s lives safer, at Metalesa we intend to go further and we want to do our bit in this ongoing process of awareness.
In today’s post we talk about the safety of cyclists when they circulate through urban areas or roads. Undoubtedly, it is one of the most vulnerable groups that suffer too many accidents, which is a problem that must be solved.
To start with, here there are some figures. In 2014, 75 cyclists died on Spanish roads, in 2015 there were 55 and in 2016 it was reduced to 33. Having said that, although the trend of cyclist accidents seemed to be decreasing in the last five years, the truth is that in May 2017, these figures were already doubled, and in 2020, 36 cyclists lost their lives, a surprising number after long months of confinement.
At the beginning of the article we mentioned that our products are intended to ensure safety. However, people must also do their part to achieve this goal. Here there are some useful tips for both cyclists and drivers to ensure the safety of those both in urban areas and on roads.

Everything a cyclist needs to know to ensure their safety
Although there may be external factors that endanger their safety, it is important that the riders know how to protect themselves:
- To know traffic regulations, and therefore, what you can do and what it is forbidden on the road will allow them to be more aware of the dangers.
- If there is no bike lane on the road, it is preferable to travel on roads with a wide shoulder, much better if they are little traveled.
- The use of conspicuous clothing is recommended to make themselves more visible. Here we also include the helmet color, which is mandatory.
- Check wheels, brakes and lights from time to time. Something as fast as a simple check-up can save a rider’s life. Regarding the lights, it is important to note that they should be used both at the front and at the rear in low light hours. In addition, it is mandatory to turn on the lights when driving through the interior of a tunnel, whatever time it is.
- Use of the rear-view mirror. This device is less common than it should be. Rather few cyclists decide to attach a rear-view mirror to their bicycle, but it is undoubtedly a very useful component to increase safety, and cheap indeed.

What must a vehicle driver take into account to ensure the safety of cyclist?
- It is important to bear in mind that, when passing a cyclist, the air displaced by the vehicle can throw him off balance. Therefore, when overtaking, at least 1.5m of lateral space must be left as a safety distance.
- If cyclists are observed, slow down and be extremely cautious.
- The horn should not be used to warn the cyclist of the presence of the vehicle because it can scare, distract and cause them a fall.
- It is very important to know when cyclists have priority. For example, a group of cyclists has priority when they have started a crossing or entered a roundabout.
- Only with greater respect for the priority of passage and the safety distance could the number of cyclist victims be significantly reduced.
We are aware that these are quite obvious pieces of advice, but it is not a bad thing to remember them considering that, statistically, most accidents occur precisely because of not complying with these simple tips.
Road Safety Improvements for cyclists through urban planning
Not only are people becoming more and more aware, so are cities, orienting their planning towards more efficient models, both in terms of safety and sustainability. In this sense, the promotion of urban mobility through the use of bicycles entails an ambitious urban reorganization that involves the implementation of cycle lanes. In fact, we are seeing that the cities deploy every day more kilometers of bike lanes.
How do we guarantee the safety of cyclists from Metalesa?
Protection is our goal. That is why we design and manufacture road safety products specially designed for this.
Our M009 cyclopedestrian railing is a restraint system for cyclists that cannot be absent in urban areas or on roads to reduce the accident rate of cyclists.
It is located at the ends of bridges or crowning walls to prevent pedestrians and cyclists from falling into the void. It differs from a normal railing in its height, between 1.3 – 1.5 meters, which prevents cyclists from exceeding it, which is perfectly possible with traditional railings for pedestrians up to 1 meter high.
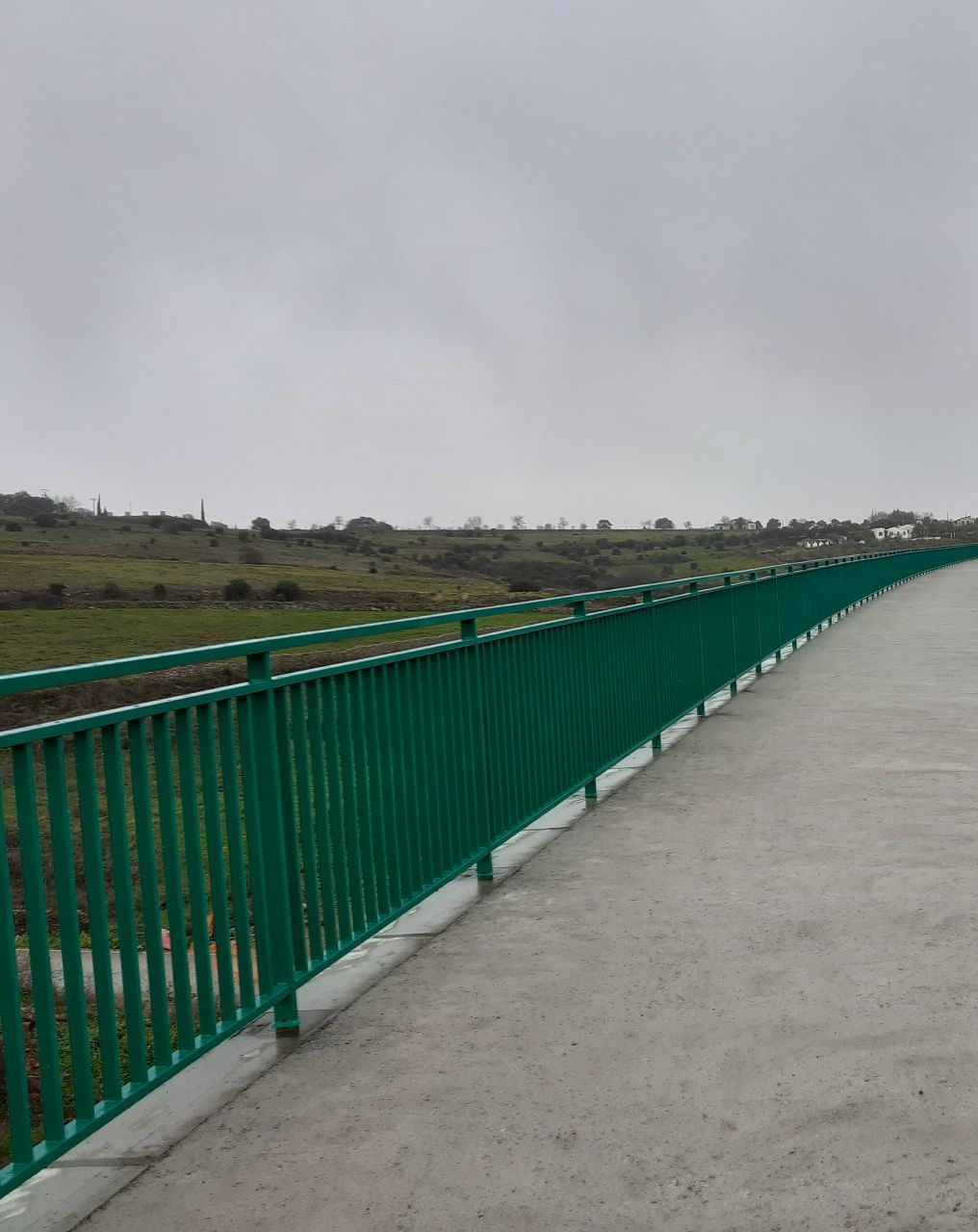

In addition, all the components of the railing are protected against corrosion at the customer’s discretion: hot galvanized, thermo-lacquered or both treatments at the same time.
The thermo-lacquering allows to facilitate the aesthetic integration of the cyclopedestrian railings with the environment, since we can paint them in any color from the RAL chart.
In a previous post we made reference to how 5G technology in cities can help ensure maximum safety. Perhaps a day will come when cyclists will cease to be a vulnerable group thanks to the development of tools based on wireless connectivity. However, at Metalesa, we obviously support technological progress and the great advances that it can bring to road safety, but we also want to take advantage of it to call for the responsibility of each one. Safety is everyone’s business!
En un post anterior hicimos referencia a cómo la tecnología 5G en las ciudades podrá ayudar a garantizar la seguridad al máximo. Quizá llegará algún día en el que los ciclistas dejen de ser un grupo vulnerable gracias al desarrollo de herramientas basadas en la conectividad inalámbrica. No obstante, desde Metalesa, evidentemente apoyamos el progreso tecnológico y los grandes avances que puede aportar a la seguridad vial, pero también queremos aprovechar para hacer un llamamiento a la responsabilidad de cada uno. ¡La seguridad es cosa de todos!